Figure 7.
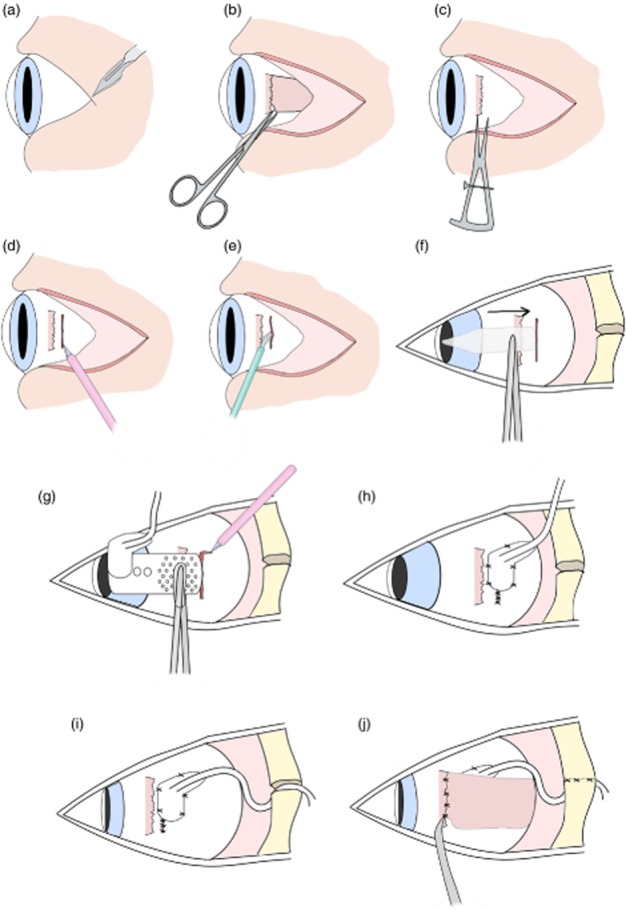
Surgical implantation of suprachoroidal retinal prosthesis in cadavers. (a) First a lateral canthotomy was created. (b) The lateral rectus muscle was detached. (c) Scleral wound placement was measured 1–2 mm posterior to lateral rectus muscle. (d) A 9-mm full-thickness scleral incision was created. (e) A pocket was made in the suprachoroidal space using a crescent blade. (f) The pocket was then probed with a lens glide to extend the space. (g) Prosthesis was inserted and then a relieving incision made to adjust placement. (h) Sclera and scleral patch were sutured using interrupted sutures. (i) The lead was then routed 15–30° superior to wound, and the orbit grommet was inserted into the orbitotomy. (j) Finally, the lateral rectus muscle was reattached with 6/0 vicryl sutures and the periosteum sutured.
