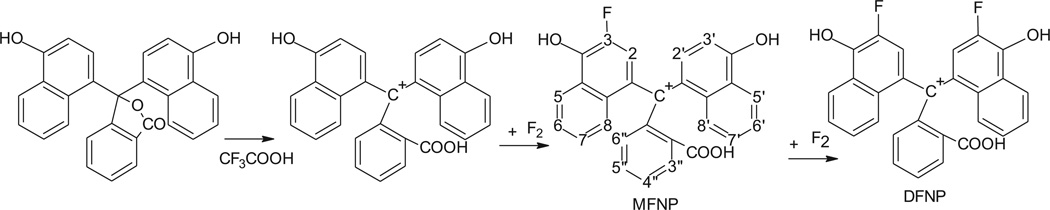
Fig. 5.
A proposed mechanism for the reaction of naphtholphthalein fluorination. Trifluoroacetic acid converts the reagent into the cation form, which can survive direct fluorination producing mono- and difluorinated products. The formula of monofluorinated derivative has a numbering scheme for the carbon atoms, which is used in the text.