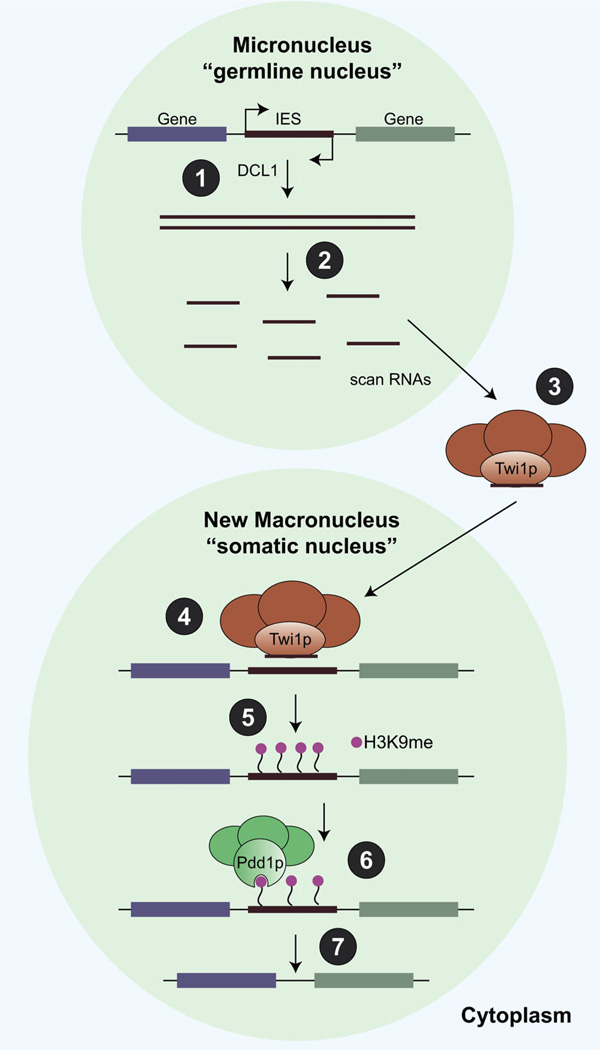
Figure 4.
The PIWI/piRNA pathway marks repeat sequences for elimination in the somatic macronucleus of Tetrahymena. (1) Bidirectional transcription in the micronucleus creates double-stranded RNAs, which are a substrate for Dicer (DCL2). (2) Long-stranded RNAs are processed into scanRNAs by a Dicer-dependent mechanism. Scan RNAs are made from all sequences in the micronucleus, but only those made against internal eliminated sequences (IES) are shown above. (3) Scan RNAs are exported from the micronucleus (germline nucleus) and bind to a protein complex that contains the PIWI homolog Twi1p. Before entering the new macronucleus (somatic nucleus), Twi1p/scanRNA complexes enter the old macronucleus and scanRNAs that have homology against the DNA are destroyed (not shown in figure). (4) Twi1p/scanRNA complexes that remain are homologous only to IES regions, and are imported into the new macronucleus. (5) The Twi1p/scanRNA complexes mark IES regions for elimination by directing H3K9 methylation. (6) The Pdd1 protein contains a chromoshadow domain, which recognizes the H3K9 methylation on IES regions and recruits the machinery required for IES excision (7) leaving behind DNA enriched only for transcribed genes.