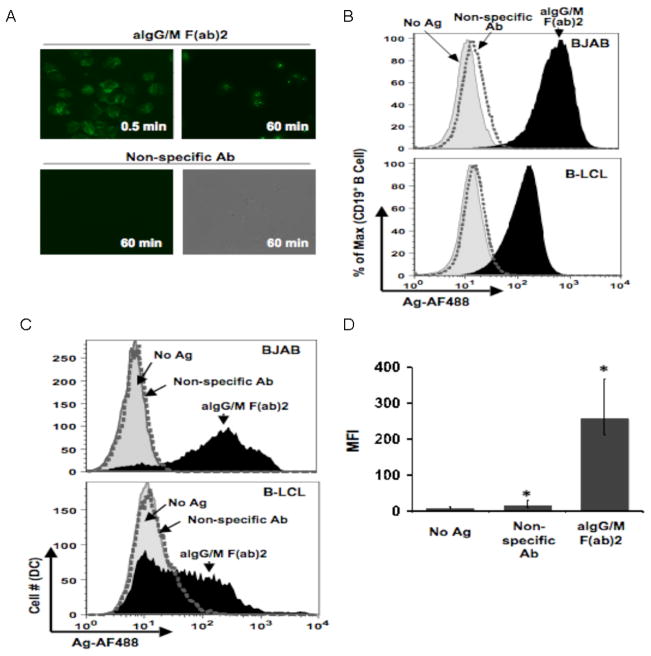
Fig. 1.
Human B cells acquire and transfer antigen to dendritic cells. (a) Kinetics of antigen uptake by B cells. B-LCL pulsed with either aIg (upper panels) or non-specific Ab (lower panels) for indicated time points, washed and observed by fluorescence microscopy (450X magnification). (b) Antigen uptake by various B cell lines. BJAB (top panel) and B-LCL (lower panel) were pulsed with no antigen (gray curve), non-specific Ab (dotted curve) or aIg (black curve) for 60 min and stained with anti-CD19 antibody for flow cytometry. (c) Various B cell lines transfer antigen to dendritic cells. Primary myeloid DCs were co-cultured for 18 hr with BJAB (top panel) or B-LCL (lower panel) pulsed with no antigen (gray shaded curve), non-specific Ab (dotted curve) or aIg (black curve). Antigen levels (AF488) were assessed for the CD19−:CD14−:CD11c+ gated population. (d) Levels of transferred antigen are significant. MFI values for transferred antigen (AF488) are given for 3 independent experiments with BJAB cells as antigen donors (* p< 0.001; n=3; thin bars represent value range).