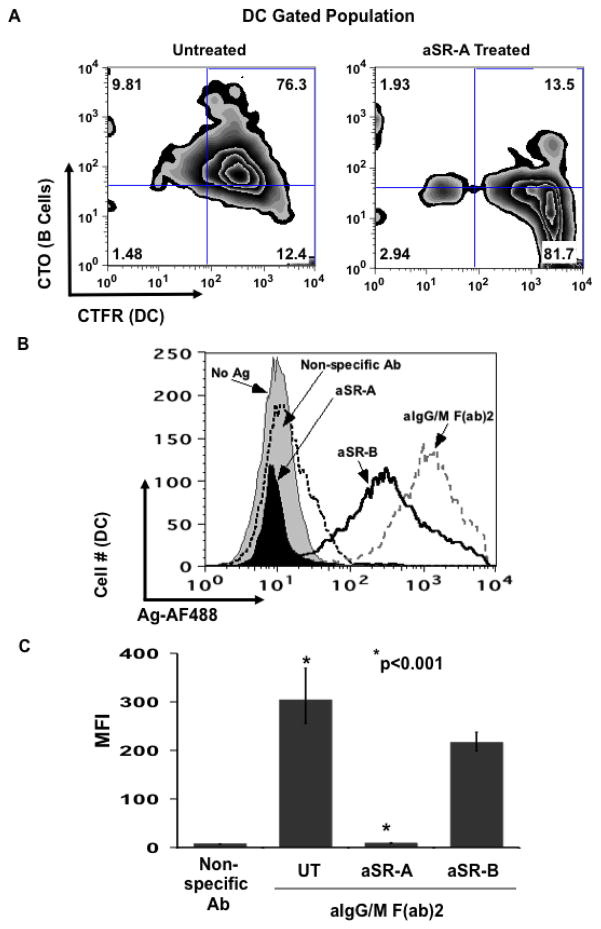
Fig. 5.
Dendritic cells acquire B cell derived membrane and/or intracellular proteins through an SR-A dependent mechanism. BJAB cells were labeled with CTO and pulsed with antigen. Primary DCs were labeled with CTFR and then left untreated (UT) or treated with either aSR-A or aSR-B blocking antibodies for 1 hr. These DCs were co-cultured for 18 hr in the presence of inhibitors with Ag-pulsed B cells. Cells were harvested and analyzed by flow cytometry. (a) B cell specific fluorescence is transferred to dendritic cells and membrane transfer is blocked by aSR-A. Level of B cell derived label (CTO) was determined for the untreated DCs (CTFR) (left panel) and aSR-A Ab treated (right panel). (b) Antigen transfer to DCs is dependent on SR-A. Levels of transferred antigen (AF488) were assessed for the CTFR+ gated DC cells that were left untreated (UT) and cultured with B cells pulsed with either non-specific Ab (dotted curve), aIg (black curve) and those DCs that were treated with aSR-A Ab (solid black curve) or aSR-B Ab (black line) and cultured with aIg pulsed B cells (gray curve). (c) Blocking SR-A but not SR-B significantly inhibits antigen transfer. MFI values for transferred antigen (AF488) are given for 4 independent experiments (* p<0.001; n=4; thin bars represent value range).