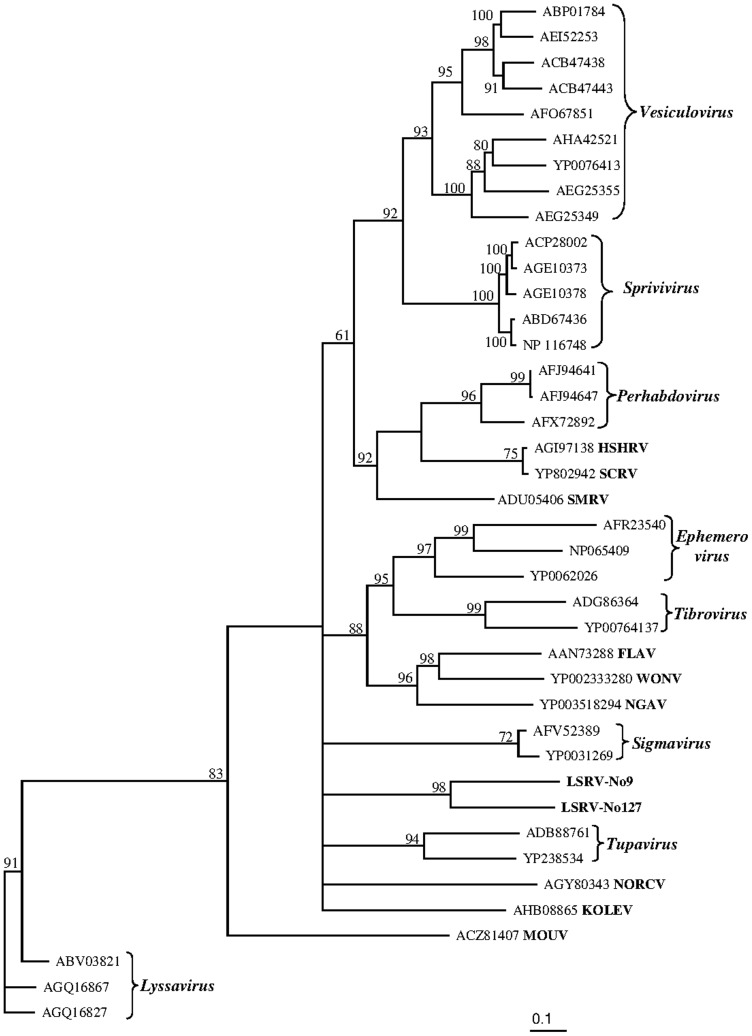
Figure 6. Phylogenetic position of two Rhabdoviridae, LSRV-No9 (Accession no: KJ958535) and LSRV-No127 (Accession no: KJ958536), obtained from salmon louse (L. salmonis) in relation to other rhabdoviruses based on analysis of the L protein sequences after removal of ambiguously aligned regions using Gblocks [38].
The evolutionary relationship is presented as maximum likelihood trees based on 1630 aa from the complete alignment of the L protein amino acid sequences. Branch lengths represent relative phylogenetic distances according to maximum likelihood estimates based on the VT matrix [39]. The scale bar shows the number of amino acid substitutions as a proportion of the branch lengths.