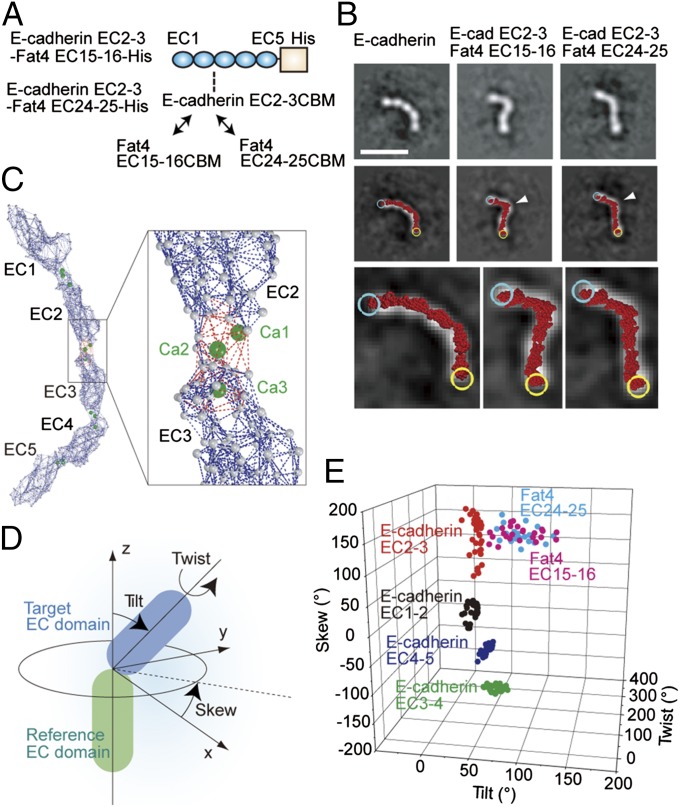
Fig. 2.
Fat4-derived CBMs cause deformation of E-cadherin ectodomain. (A) Schematic drawing of the mutated E-cadherin ectodomain in which the CBM of EC2-3 is replaced with that of Fat4 EC15-16 or Fat4 EC24-25. (B) Representative views of the wild-type and CBM-substituted E-cadherin (Top) in class averages, and atomic model fitting (Middle). The molecular images were overlaid with fitted atomic models (red), which are enlarged to show individual amino acid residues at the bottom. Cyan and yellow circles represent the N and C termini of the atomic models, respectively. White arrows point to the position where CBMs were replaced. (Scale bar, 20 nm.) (C) Elastic network model of E-cadherin ectodomain. Gray balls represent amino acid residues. Dark blue and red dotted lines indicate the springs connecting amino acid residues. The red dotted lines were eliminated in the non–Ca2+-binding EC–EC linkers. (D) Geometric definition of a target EC domain against the reference EC domain. (E) Scattergram of EC–EC linkage geometries in wild-type and mutated E-cadherins.