Fig. 1.
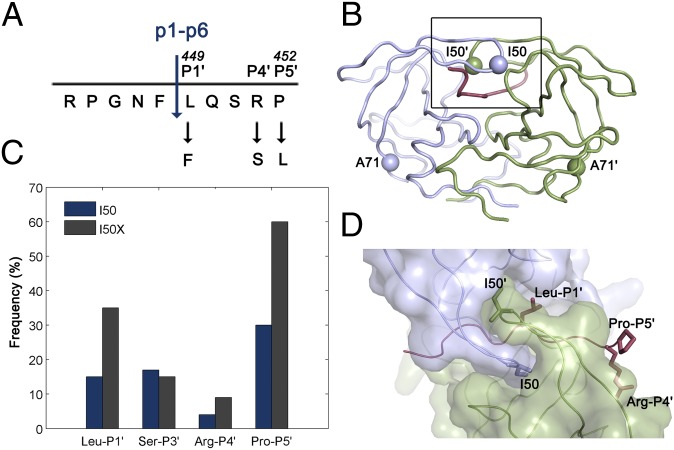
HIV-1 protease and p1-p6 cleavage site coevolution with I50V primary drug resistance mutation. (A) p1-p6 cleavage site sequence and the most common coevolution mutations at P1′, P4′, and P5′ sites. (B) Residues 50 and 71 are indicated as spheres on the homodimeric HIV-1 protease structure. (C) Frequency of mutations in the p1-p6 cleavage site without (dark blue) and with (gray) any mutations at position 50 of the protease. The difference is statistically significant for LP1′, RP4′, and PP5′. Data from ref. 26. (D) Side chains of the substrate residues LP1′, RP4′, and PP5′ and the protease residue I50 are shown as sticks. Monomers of HIV-1 protease are in light purple and green, and the substrate is red in B and D.