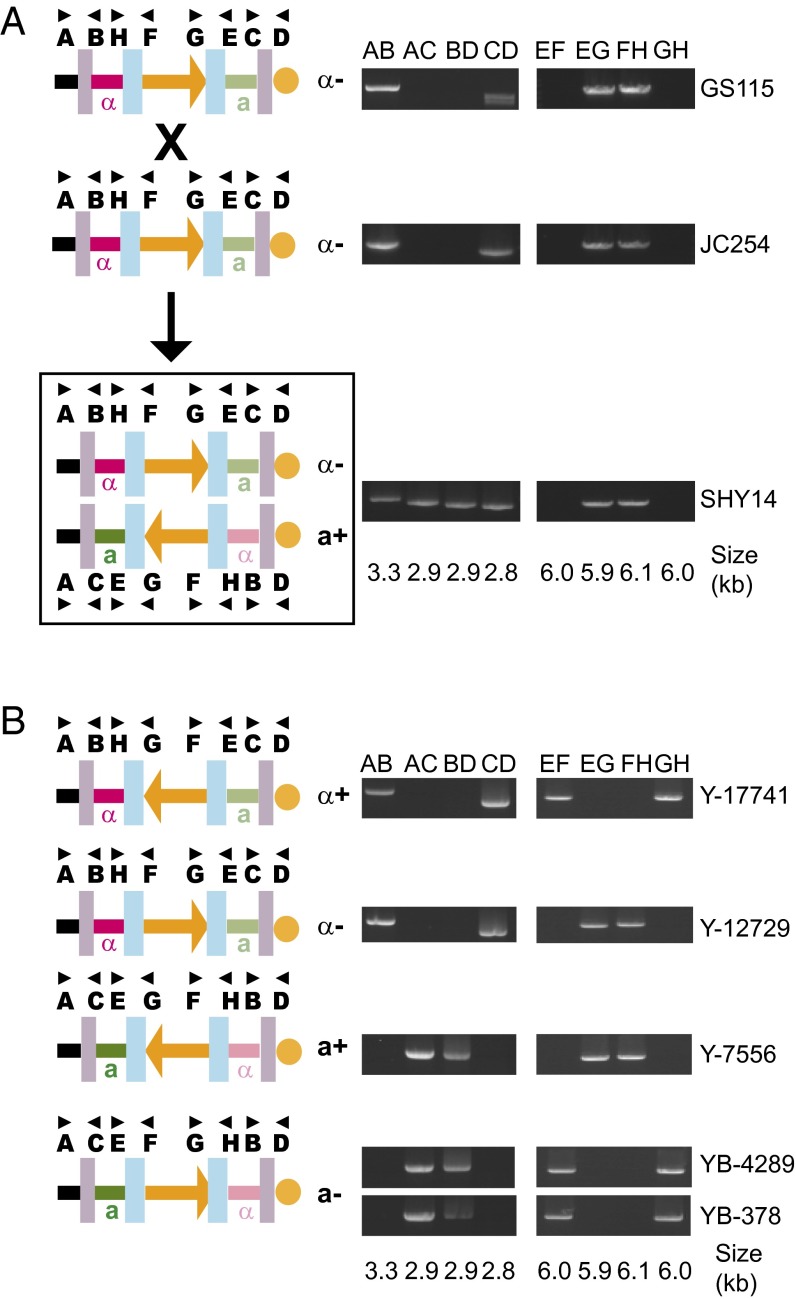
Fig. 5.
Mating-type switching by inversion in P. pastoris. (A) Crossing two strains in the same orientation results in diploids that are heterozygous for orientation. (Left) The schematic indicates chromosome 4 organization in the haploid parents and their diploid progeny. The orange arrow shows the orientation of the 123-kb region between the inner IRs. The MAT locus closer to the telomere (orange circle) is repressed (pale colors). Purple and blue boxes represent the outer and inner IRs, respectively. (Right) Gel images show amplification across the IRs using primer combinations as indicated. (B) All four possible structures of chromosome 4 are found among natural isolates of P. pastoris. The isolates are from tree fluxes and were obtained from the US Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service collection as Komagataella phaffii (SI Appendix, Table S2).