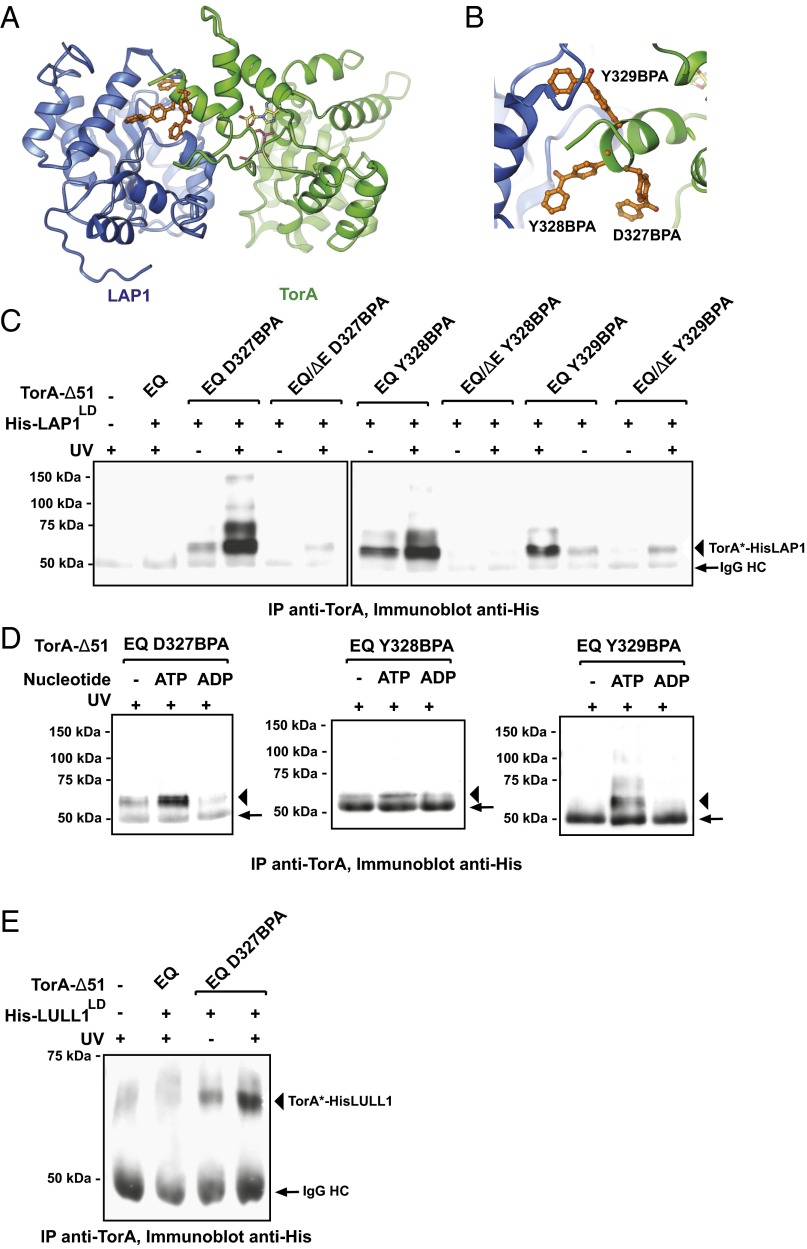
Fig. 3.
Site-specific cross-linking between TorA and LAP1/LULL1. (A) Predicted interface between LAP1 (blue) and TorA (green). Cross-linker pBPA (orange) was installed on TorA at three sites (D327BPA, Y328BPA, and Y329BPA) at the predicted interface with LAP1. (B) Zoomed-in view of TorA and LAP1 interface. TorA D327BPA, Y328BPA, and Y329BPA are shown in orange. (C) HIS-LAP1LD and TorA-Δ51 constructs were copurified from E. coli in 1 mM ATP. Copurified complexes were incubated at 30 °C for 5 min, cooled to 20 °C, and UV-irradiated for 15 min. Cross-linked species were immunoprecipitated with a TorA antibody, resolved by SDS/PAGE, and analyzed via immunoblotting using HIS antibody to detect LAP1. Arrows indicate the Ig heavy chain, and arrowheads indicate the TorA-LAP1 cross-linked species. Note that the order of loading (±UV) was inadvertently reversed for Y329BPA. IP, immunoprecipitate. (D) Copurified HIS-LAP1LD and TorA-Δ51 constructs were treated with CIP overnight at 4 °C to remove nucleotide. ATP or ADP (10 mM) was added back to the cross-linking reaction. Cross-linked species were analyzed as described in C. (E) As in C, but for HIS-LULL1LD.