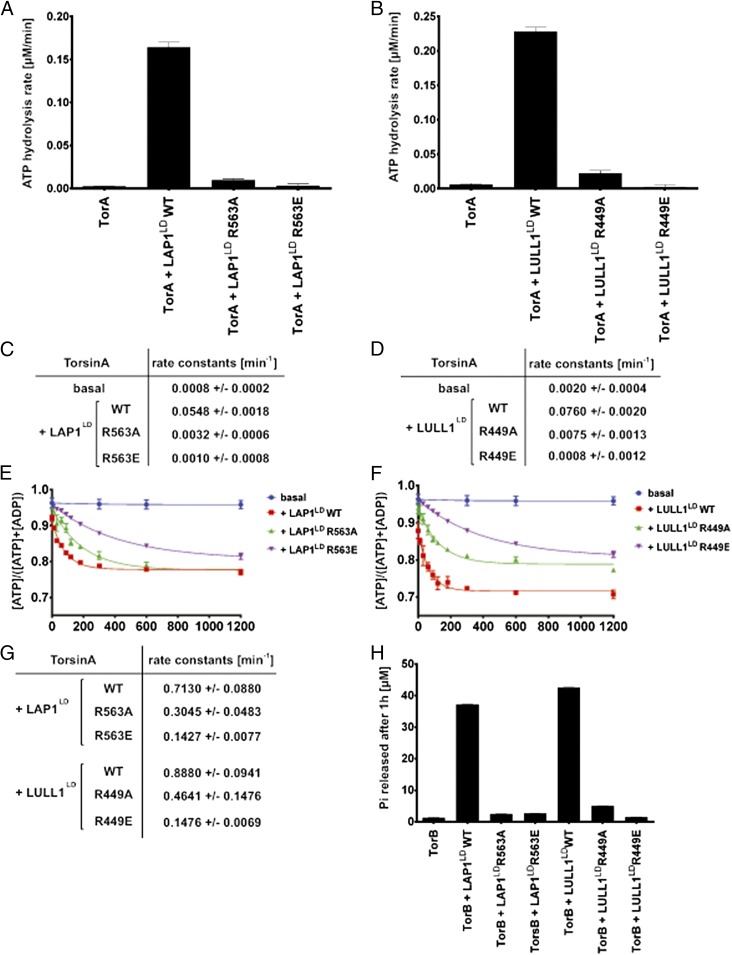
Fig. 6.
LAP1 and LULL1 Arg mutants fail to stimulate TorA’s ATPase activity. (A and B) TorA ATP hydrolysis rates in the presence of WT or Arg mutant cofactors. ATP hydrolysis rates were measured as a function of Pi-production over time. TorA (3 μM) was incubated with ATP (2 mM) at 37 °C, either alone or with 3 μM indicated WT or mutant cofactor, and Pi-production was measured at various time points using a malachite green assay. Data were fit with a linear regression in Prism (GraphPad) to yield the ATP hydrolysis rate. (C and D) Rate constants were obtained by dividing the ATP hydrolysis rate by the TorA concentration. (E and F) ATP single-turnover kinetics of TorA in the presence of WT or Arg mutant cofactor. Each data point represents the mean of three independent experiments. Error bars indicate SD. (G) Rate constants were obtained by fitting the data from E and F with a single exponential decay function in Prism. TorA basal ATP hydrolysis could not be fit to a single exponential decay function in a statistically significant manner. (H) LAP1 R563 and LULL1 R449 are required to stimulate TorB’s ATPase activity. TorB (3 μM) was incubated with ATP (2 mM), either alone or with 3 μM WT or Arg mutant cofactor. ATP hydrolysis was measured as a function of Pi-production after 60 min using a malachite green assay.