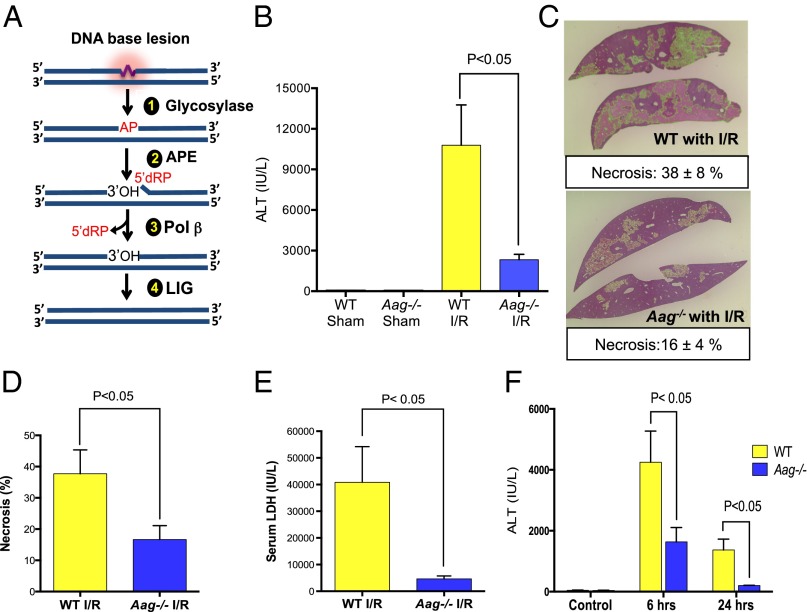
Fig. 1.
Aag deficiency protects liver against I/R-induced tissue damage. (A) The BER pathway initiated by various DNA glycosylases consists of four key enzymatic steps: (i) glycosylase-mediated excision of a damaged base generating an abasic site; (ii) incision of the sugar-phosphate backbone at the abasic site by APE, yielding a 3′-OH adjacent to a 5′-dRP moiety; (iii) 5′-dRP removal and DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase β (Pol β); and (iv) sealing of the DNA nick by DNA ligase (LIG). (B) Serum ALT concentrations after 90 min of ischemia and 24 h of reperfusion (n = 3 in sham groups and n = 7–8 in I/R groups). (C) Representative images of necrotic areas 24 h after I/R in Aag−/− (n = 7) or WT livers (n = 8); liver sections (4 μm) were stained with H&E. (D) Mean necrotic area in ischemic liver samples and (E) serum LDH concentrations 24 h after reperfusion (n = 3 in sham groups and n = 7–8 in I/R groups); necrosis analyzed by ImageJ (necrotic areas indicated by green color). (F) Serum ALT in control mice (no surgery) or after 60 min of ischemia plus either 6- or 24-h reperfusion in WT and Aag−/− mice. Error bars represent the mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments.