Figure 1.
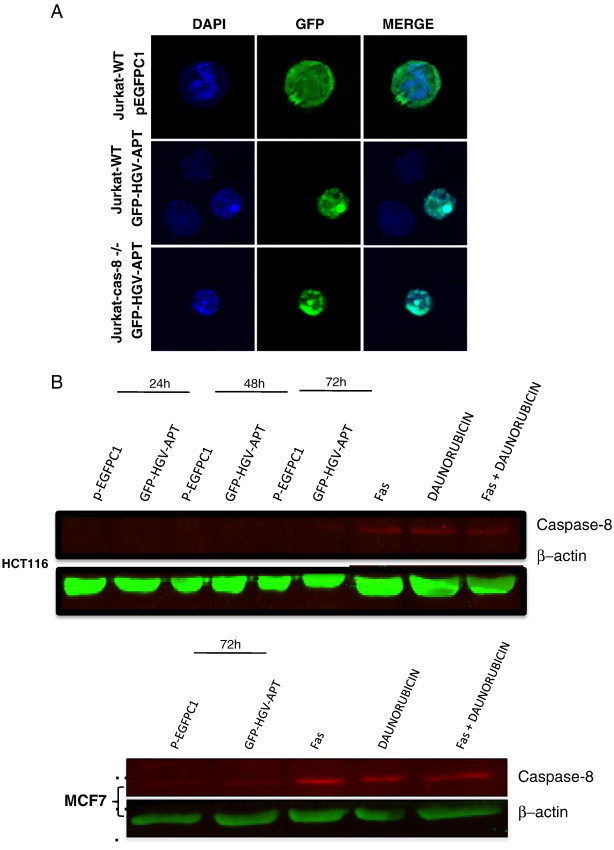
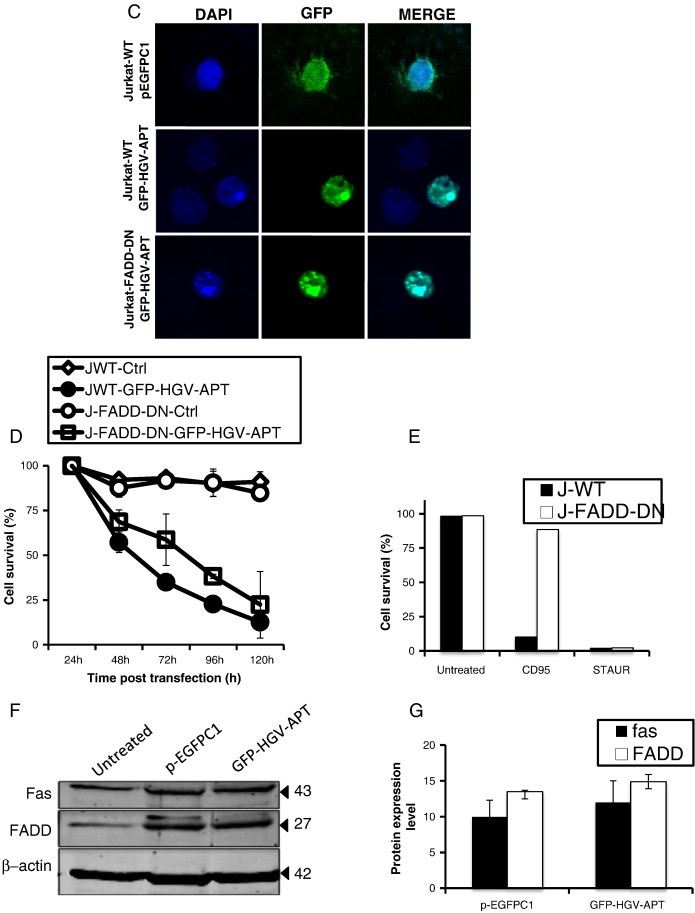
HGV-Apoptin mediated cell death is independent of the death receptor pathway. A) Cellular localization and morphological changes induced by HGV-Apoptin in Jurakt WT or Jurkat caspase-8-/- cells. Cells were transfected by electroporation with GFP-HGV-APT and the corresponding pEGFPC1 control plasmid, cells were fixed 48 h post transfection and stained with DAPI for the detection of nuclear morphology. B) HGV-Apoptin does not activate caspase-8. Western blot analysis of cell lysates from HCT116 (colon carcinoma) and MCF7 cells transfected either with pEGFPC1 or with GFP-HGV-APT for caspase-8 activation. At the indicated time points post-transfection, GFP positive cells were sorted by flow cytometry; cells treated with anti-FAS activating antibodies, or, Daunorubicin or both represent a positive control. C) Detection of apoptosis induced by HGV-Apoptin in Jurkat WT cells or Jurkat FADD-DN. Cells were transfected by electroporation with GFP-HGV-APT or the corresponding pEGFPC1 control plasmid. 48 h later, transfected Jurkat cells were fixed and stained with DAPI for the detection of nuclear morphology. D) Quantification of cell survival in Jurkat WT and Jurkat FADD-DN as percentage of PO-PRO/7AAD double negative cells (cell survival) in the GFP-positive population from 24 to 120 h post-transfection. E) Control experiment to assess cell death mediated by CD95/FAS, both Jurkat WT and FADD-DN cells were treated with anti-FAS (IgM) antibody or with Staurosporine (STAUR), and cell death was measured by flow cytometry after 12 h. F) Western blot analysis of FAS and FADD level of expression in Jurkat cells 48 h post transfection with GFP-HGV-APT or the corresponding pEGFPC1 control vector. In panels “B” and “F” β − actin was used as a protein loading control. G) Quantification of the level of expression of FAS and FADD 48 h post-transfection (Western blot shown in “G”).
