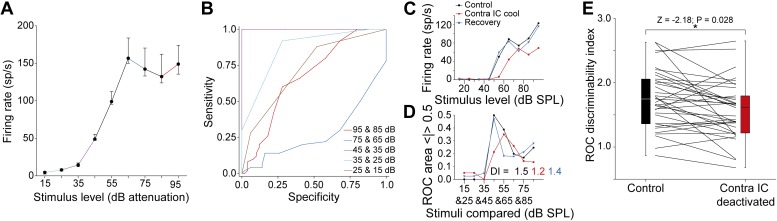
Figure 6. Deactivation of the contralateral IC reduced sound level discriminability in the IC.
(A) Control RLF of an IC neuron (median ± IQR). (B) ROC pairwise analysis of the responses in (A) with colors of ROC curves matching the corresponding paired values in (A). (C) An example RLF (black) which showed a reversible reduction in rate and slope on deactivation (red) that recovered to control values (blue). (D) A ‘discriminability index’ (DI) was calculated from the change in area under the ROC (see text) for each adjacent stimulus pair in each condition. The reduction in rate and slope in (C) on deactivation resulted in a reduction in DI from 1.5 to 1.2 with recovery to 1.4. (E) The median DI for the population of RLFs declined on deactivation of the contralateral IC, indicating a reduction in discriminability of sound level on in the absence of commissural input.