Figure 3.
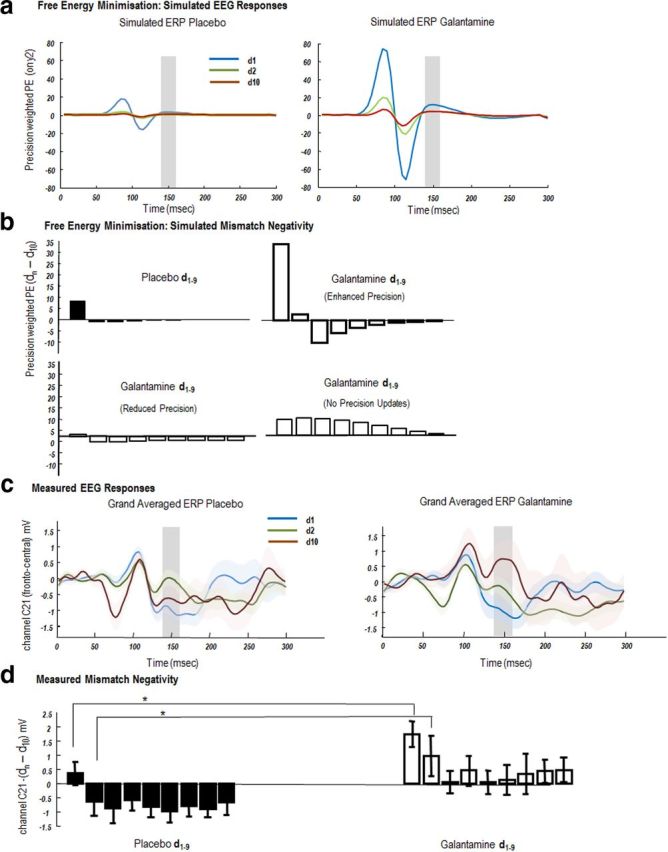
EEG responses: simulated and measured. a, Simulated ERPs evoked by tones whose frequency deviates from preceding tones (d1) and are repeated until the tenth presentation (d10). These ERPs are the precision-weighted prediction errors (Fig. 1) of sensory data encoding the frequency of the tone (y2). Left, Simulated precision-weighted prediction error under placebo (d1, blue; d2, green; d10, red). The agent learns the tone frequency over successive repetitions, resulting in a reduction in the size of the evoked responses. Right, A similar profile is observed under galantamine, with elevated priors on sensory precision. Evoked responses are higher in magnitude and sustained for longer (d2). b, Top, Simulated mismatch response (d10 − dn), where d10 is set as the standard and d1–d9, a parametric deviant. The MMN is taken from the ERPs illustrated in a. It is simply the difference between simulated evoked responses (precision-weighted prediction errors) between standards and deviants summed from 140 to 160 ms (shaded areas). Left, The placebo MMN shows a rapid one-shot learning, with a smaller MMN on d1 and a reversal in MMN polarity on d2, which returns to close to 0 at d9. Right, Galantamine MMNs are prolonged and have greater magnitude for all trials. Bottom, Two alternate MMN effects under different galantamine models (left) where galantamine reduced sensory precision and (right) where galantamine prevents precision updating over trials. c, Scalp EEG measurements of auditory evoked potentials. Grand-averaged waveforms from a single frontocentral electrode (C21) for the presentation of the first deviant tone in a sequence (d1), second tone (d2), and final tone (d10), averaged across tones of all frequencies, under placebo (left) and galantamine (right). MMN effects are evident in both drug conditions ∼150 ms. d, The MMN effect across all nine tone repetitions (d10 − dn). The MMN effect was significantly different across repetitions and drug state. In particular both d1 and d2 induced MMNs were greater on galantamine than on placebo.
