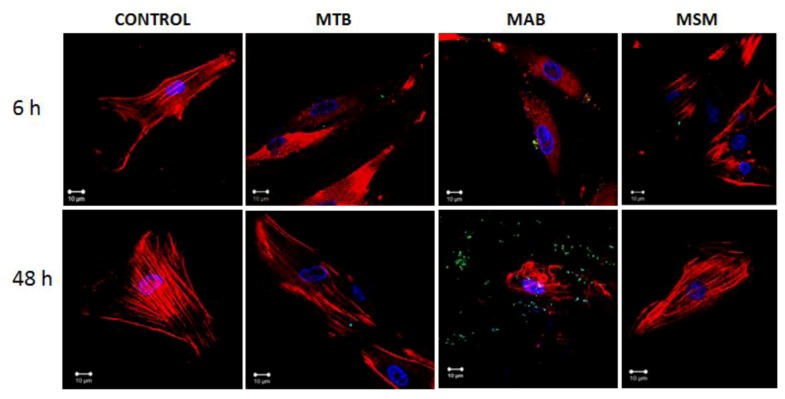
Figure 3.
Mycobacterial infection induces changes in the distribution of the actin filaments in the limbo-corneal fibroblasts. The actin filaments were stained with phalloidin-TRITC, and the mycobacteria were stained with FITC. The uninfected cells (CONTROL) exhibit a longitudinal distribution of the actin filaments. The cells infected with MTB exhibit notable changes in the spatial distribution of the actin filaments, most evident at 6 h post-infection. MAB infection produced a loss of the longitudinal distribution of the actin filaments; focal points are visible in the cellular cytoplasm at 6 h post-infection, and the heterogeneous and disorganized distribution of the actin filaments is observed at 48 h. In contrast, the distribution of the actin filaments in the cells infected with MSM did not exhibit significant changes at 6 h and 48 h post-infection.