Table 1.
Alteration in goblet cells and mucins responses during common enteric infections.
| Enteric Infection | Goblet Cell & Mucin Response | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parasitic Infection | Helminth Infection | ||
| N. brasiliensis | Goblet cell hyperplasia;  Muc2, Muc2, |
[39,40,44,45] | |
 sulfated mucins sulfated mucins | |||
| T. spiralis | Goblet cell hyperplasia;  Muc2/3 Muc2/3 |
[43] | |
| T.muris | Goblet cell hyperplasia;  Muc2/4/13/17, Muc2/4/13/17,  charged mucins charged mucins |
[37,38,95] | |
| Protozoal Infection | |||
| E. histolytica |
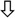 Mucins Mucins |
[56] | |
| Bacterial Infection | C. Rodentium |
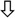 Mucins Mucins  Muc1 Muc1 |
[96] |
| H. pylori |
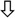 Muc6/5ac, Muc6/5ac,  Muc4 Muc4 |
[61,97,98] | |
| C. jejuni |
 Muc1 Muc1 |
[103] | |
| Viral Infection | Rota virus |
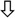 Goblet cell (early time points); Goblet cell (early time points); |
[79] |
 Muc2, Muc2, 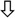 sulfated mucins sulfated mucins |
