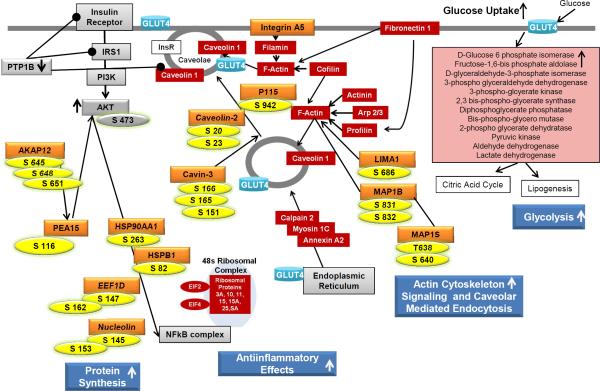
Figure 3.
Overview of identified PMI 5011 effects on human skeletal muscle culture derived from biopsies from obese, insulin resistant individuals. Global phosphoproteomics data from the current study (protein name: orange, phosphorylation sites: yellow) are overlaid onto results from previous studies [13-16]. Proteins listed in red boxes are involved in actin cytoskeleton signaling and caveolar mediated endocytosis and glycolysis and were identified to be up-regulated due to PMI 5011 treatment in global proteomic analysis [16]. Proteins listed in gray boxes were also identified to be regulated due to PMI 5011 treatment in previous studies [13,14]. Phosphoproteomics data from this study show that PMI 5011 increases phosphorylation of proteins involved in protein synthesis, actin cytoskeleton signaling, and translocation of proteins such as GLUT4 to the plasma membrane. Combined, these data show that PMI 5011 improves insulin signaling and GLUT4 translocation to the plasma membrane, resulting in increased glucose uptake and utilization, thereby ameliorating insulin resistance.