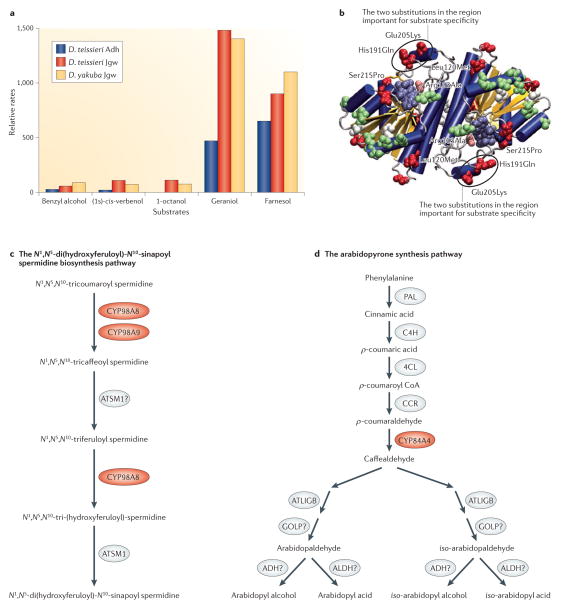
Figure 1. Several new genes evolved novel biochemical functions.
a | The protein Jingwei (Jgw) encoded by African Drosophila spp.7 is a dehydrogenase enzyme that has evolved altered substrate specificity compared with the ancestral Alcohol dehydrogenase (Adh). Compared with the parental enzyme, Jgw can use long-chain primary alcohols more efficiently; in particular, Jgw has greater activities than the ancestral Adh towards farnesol (which is involved in juvenile hormone biosynthesis) and geraniol (which is involved in recruitment pheromone biosynthesis)17. b | The locations of the substitutions on the structure of the dimeric Adh. c,d | Three recent duplicates in the cytochrome P450 family in Arabidopsis thaliana led to the assembly of a new pathway of N1,N5-di(hydroxyferuloyl)-N10-sinapoyl spermidine biosynthesis (the new duplicates CYP98A8 and CYP98A9 are shown in red)19 (part c) and a pathway for arabidopyrone biosynthesis (the young duplicated enzyme CYP84A4 is shown in red)20 (part d). D. teissieri, Drosophila teissieri; D. yakuba, Drosophila yakuba. Parts a and b are modified, with permission, from REF. 17 © (2004) US National Academy of Sciences.