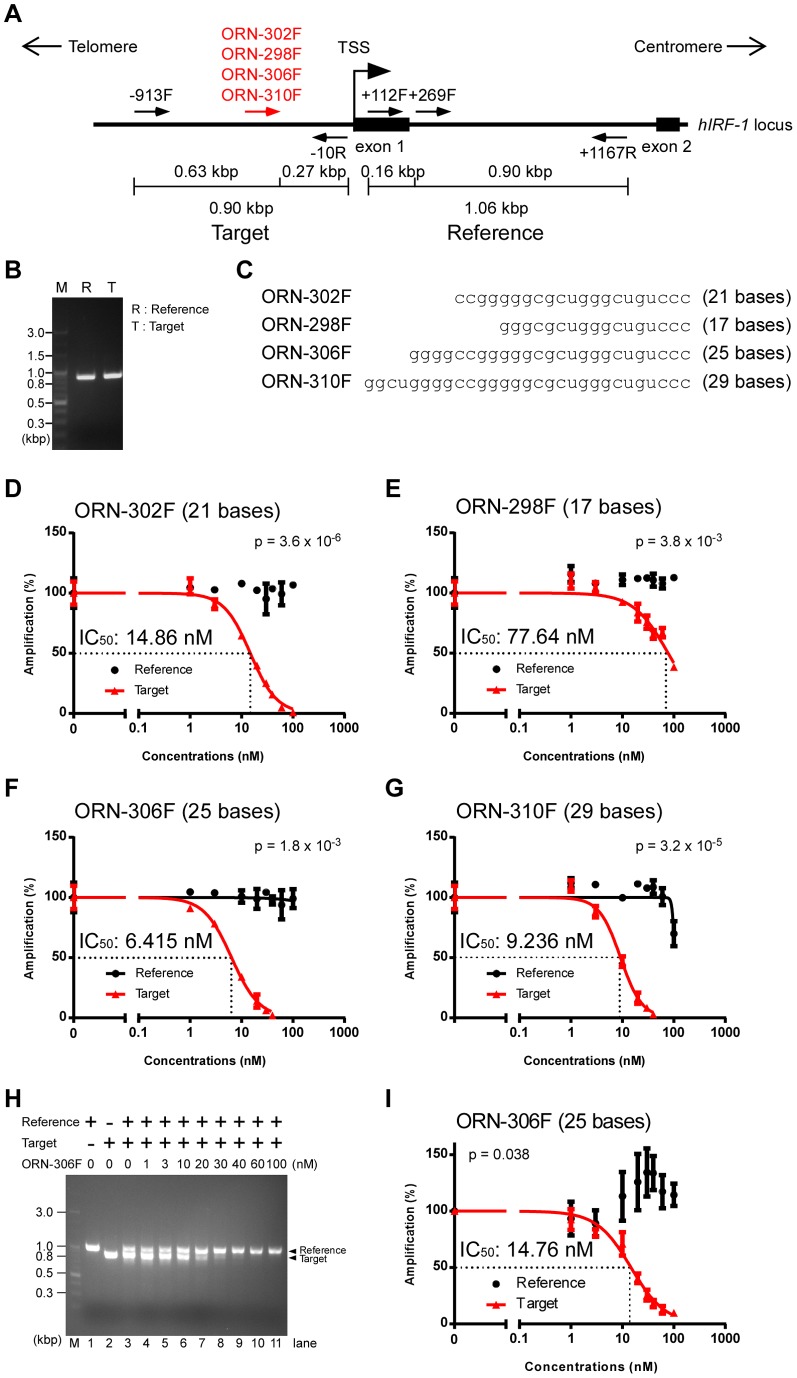
Figure 1. Inhibition of PCR amplification by ORNs of various lengths.
(A) Positions of oligoribonucleotides (ORNs) in the target region. Primers were designed against the human IRF-1 locus to amplify two neighboring regions. (B) Comparable amplification of the target and reference regions in the IRF-1 locus. (C) Alignment of ORNs (5′–3′) of various lengths. (D–G) Dose responses of ORNs of various lengths. Real-time PCR amplification in the presence of various concentrations of ORNs was normalized against the value in the absence of ORNs. Dose-response curves were generated using the Prism software; Prism was not able to generate curves of the references for ORN-302F (D) and −298F (E). Data are represented as means ± S.D. (n = 3). (H) Suppression of amplification of the target template by ORN-306F in a reaction in which the target and reference primers were mixed. (I) Dose responses calculated for the condition used in (H). P-values for the differences in amplification between the reference and the target at an ORN concentration of 10 nM were calculated using Student’s t-test (D–G, I).