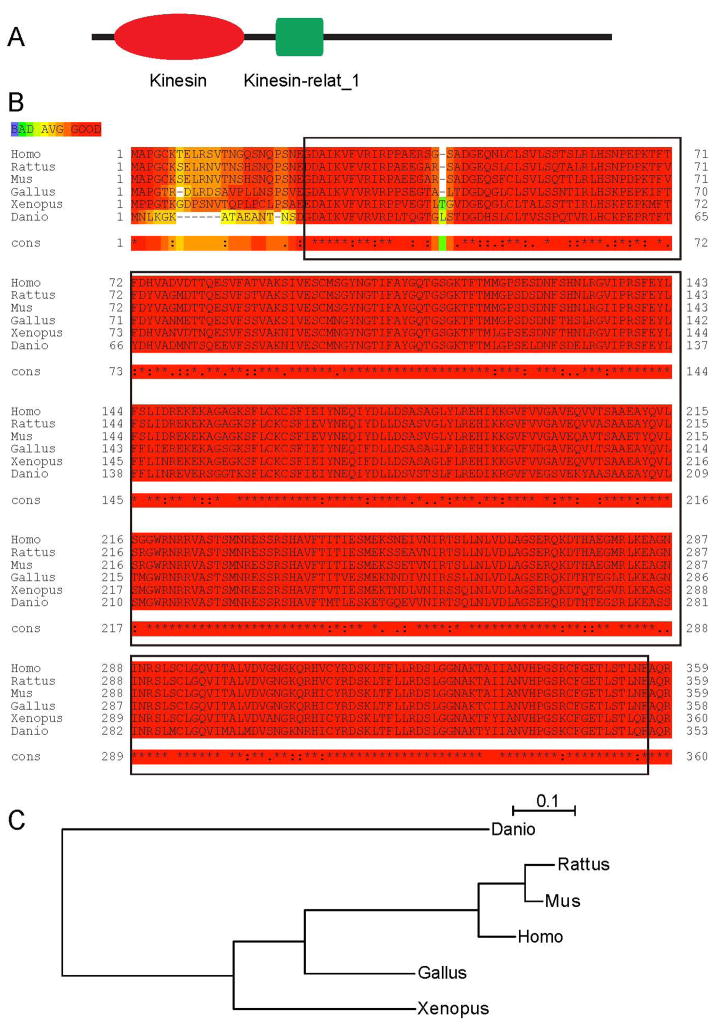
Figure 1.
Functional domains of kinesin-12 are highly conserved during vertebrates. (A)The kinesin-12 sequence is comprised of two conserved domains: kinesin-12_head (motor domain) showed in red, and kinesin-12 stalk showed in green. (B)Alignment of kinesin-12 motor domain amino acid residue sequences of Danio rerio (XP_002666969.1), Xenopus laevis (NP_001081543.1), Gallus gallus (XP_418807.2), Mus musculus (NP_034750.1), Rattus norvegicus (NP_853666.1) and Homo sapiens (NP_064627.1) kinesin-12. The sequences are retrieved from NCBI Protein sequence database. The sequences accessions IDs are labeled in brackets. These protein sequences were aligned using ClustalW2 program. This domain sequence is indicated in red rectangle.(C) Phylogenetic tree of amino acid sequences generated by using the PhyML software (Guindon et al., 2010).