Figure 1.
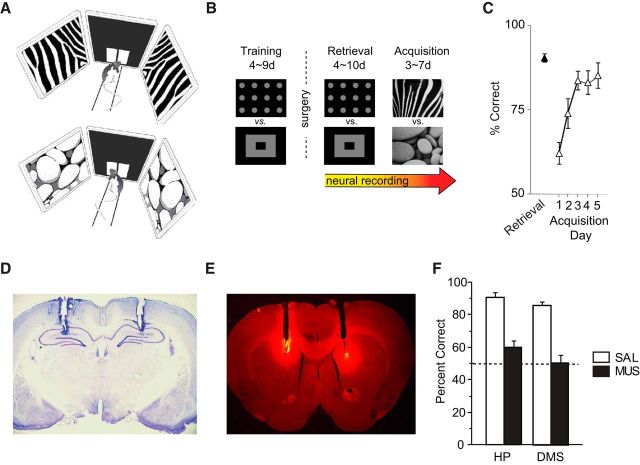
Visual scene memory task and performance deficits with hippocampal and DMS inactivations. A, Illustration of the behavioral task. The start box is not shown. The rat was required to touch between left and right discs by using the visual scene stimuli (top: zebra-striped pattern; bottom: pebbles pattern) presented in the peripheral LCD screens as a cue. B, Experimental schedules. After surgery, neural recordings were made using the same stimuli used during the training period for several days (retrieval), followed by recording with novel scene stimuli (acquisition). C, Behavioral performance. Performance dropped initially when familiar visual backgrounds (retrieval) were replaced with novel visual stimuli (acquisition), but rats quickly relearned the task in 3 d on average. Data are mean ± SEM. D, Cannula positions in the dorsal hippocampus. Data from Kim et al. (2012). E, Cannula positions and the diffusion of fluorescent muscimol in the DMS. F, Performance with either saline (SAL) or muscimol (MUS) injected in the dorsal hippocampus (HP) or in the DMS. The dotted line represents chance-level performance. Hippocampal data are from our previous study (Kim et al., 2012). Note the severe deficits when either the hippocampus or DMS was inactivated with muscimol compared with the vehicle conditions. Data are mean ± SEM.