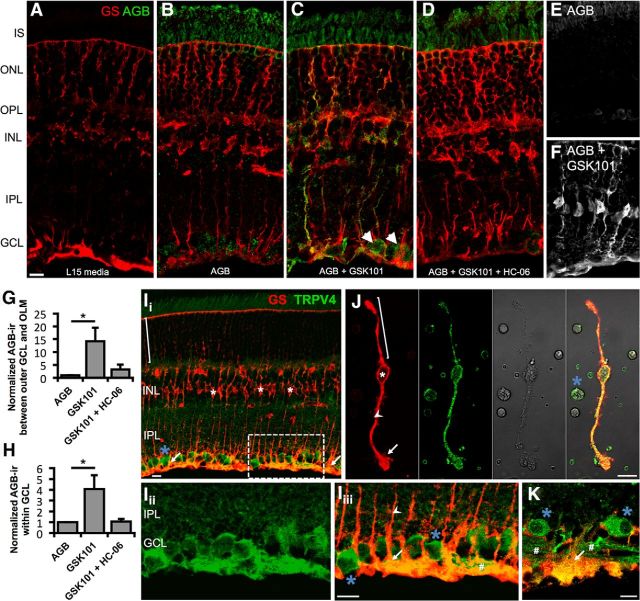
Figure 1.
TRPV4 mediates cation influx in Müller glia and RGCs. A–D, Vertical cryosections of mouse retinas immunolabeled for Müller glia marker GS (red) and AGB (green). Freshly isolated retinas were incubated for 10 min at 37°C with the indicated conditions. A, Negative control (L15 media alone; n = 2). B, Retinas incubated with AGB (N = 3). Basal cation (AGB+) influx takes place in RGCs and photoreceptors. C, GSK101 (100 nm) induces cation influx in RGCs (arrowheads) and a subset of Müller glia (n = 3). D, Agonist-induced cation entry is suppressed by HC-06 (1 μm; n = 3). E, F, Additional examples of cation influx in the absence (E) and presence (F) of GSK101. G, H, AGB influx between the outer edge of the GCL and the outer limiting membrane (OLM) (G) or within the GCL (H) was quantified by measuring the mean value (optical density) of AGB-ir. Ii–Iiii, Vertical cryosection of mouse retina immunolabeled for the Müller cell marker GS (red) and TRPV4 (green) (Ii). TRPV4 is preferentially localized to the inner limiting membrane region that contains the processes of protoplasmic astrocytes, Müller cell endfeet (arrows), and RGCs (blue asterisk). Müller cell somata (white asterisk) lack TRPV4 in intact retinas. An example distal stalk/distal end is indicated with a bracket. Iii, Iiii, Close-up of Ii (dashed rectangle) showing TRPV4 (Iii) and the merge (Iiii). J, TRPV4-ir is present throughout acutely dissociated Müller cells and a presumed RGC soma. Proximal stalk indicated by arrowhead. K, In a human retina section, TRPV4 similarly localizes to endfeet and proximal stalks of Müller glia as well as RGC somata and axon bundles (#). Scale bars, 10 μm. I, Inner; O, outer; S, segments; N, nuclear; P, plexiform; L, layer; GC, ganglion cell. *p < 0.05.