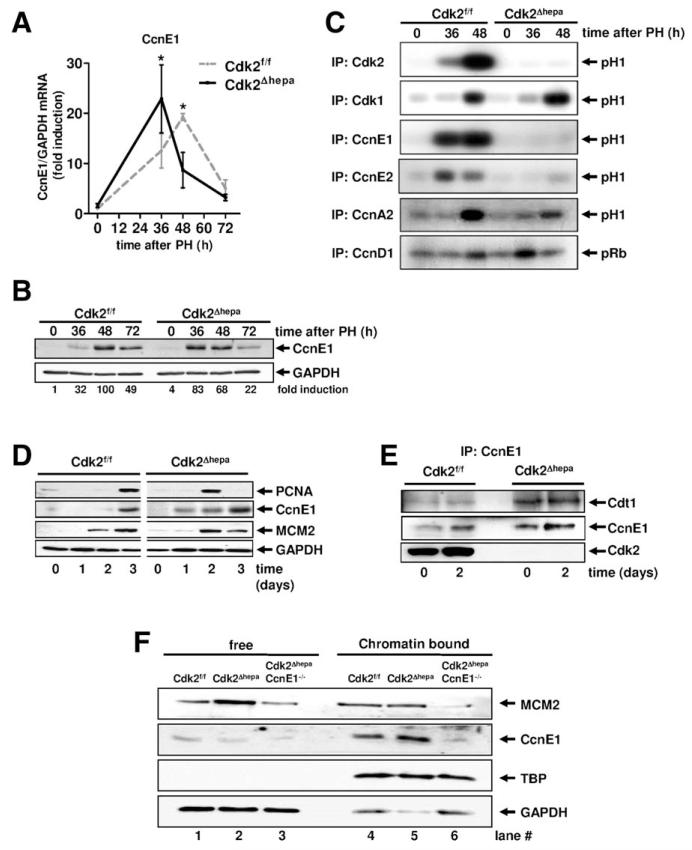
Fig. 1.
CcnE1 mediates kinase-independent functions in hepatocytes and is essential for MCM2 loading on chromatin in the absence of Cdk2. (A and C) Cdk2f/f and Cdk2Δhepa mice were subjected to PH and sacrificed at indicated time points. (A and B) Gene and protein expression profile of CcnE1 after PH. *P < 0.05. Protein levels (fold induction) were quantified using electronic densitometry and normalized to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) expression. (C) Liver extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with antibodies directed against indicated cyclins and Cdks. Precipitated cyclin/kinase complexes were used for in vitro kinase assays using recombinant histone H1 (H1) or Rb as substrate. Phosphorylated proteins are highlighted by arrows. (D and F) Primary mouse hepatocytes were isolated from indicated strains (Cdk2f/f, Cdk2Δhepa, or Cdk2ΔhepaCcnE1−/−) and cultured for up to 3 days in the presence of EGF and insulin. (D) Total protein expression of PCNA, CcnE1, and MCM2. (E) CcnE1 complexes were isolated from total proteins by IP (CcnE1) and probed for Cdt1, CcnE1, and Cdk2. (F) Expression and cellular localization of MCM2 and CcnE1 was analyzed by western blotting using fractionated cell extracts representing whole cytoplasmic protein (free) or the chromatin-bound proteins, respectively. TATA binding protein (TBP) and GAPDH represent loading controls for chromatin and cytoplasmic fractions, respectively.