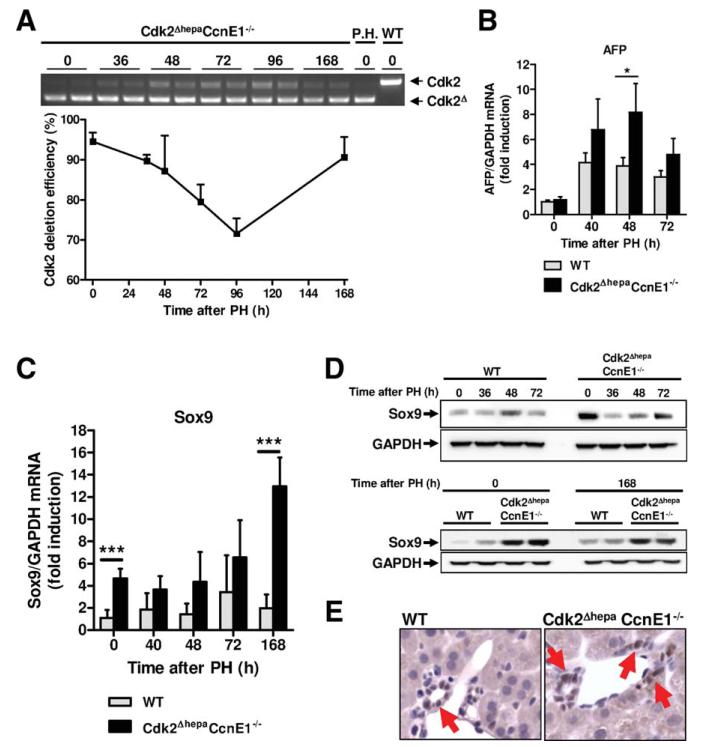
Fig. 5.
Transient Cdk2 reexpression in Cdk2ΔhepaCcnE1−/− liver after PH is associated with up-regulation of progenitor cell markers. (A) Cdk2ΔhepaCcnE1−/− mice were subjected to PH. At indicated time points, Cdk2 deletion efficiency was determined from complementary DNA using primers specific for exon 1 and 4, respectively. Upper band: WT Cdk2 gene expression; lower band: truncated Cdk2 lacking exon 2. Deletion efficiency was calculated by digital quantification of WT and KO bands. P.H., primary hepatocytes derived from Cdk2Δhepa mice were used as positive control for complete Cdk2 deletion. (B and C) Gene expression profile of AFP and Sox9 in WT and Cdk2ΔhepaCcnE1−/− mice post-PH was determined by qPCR. For each group, 3-5 animals were analyzed. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001. (D) Protein expression profiles of Sox9 in WT and Cdk2ΔhepaCcnE1−/− mice before and after PH. (E) Sox9 staining of liver sections from untreated WT and Cdk2ΔhepaCcnE1−/− mice. Sox9-positive cells show brown nuclear staining and are highlighted by arrows.