Abstract
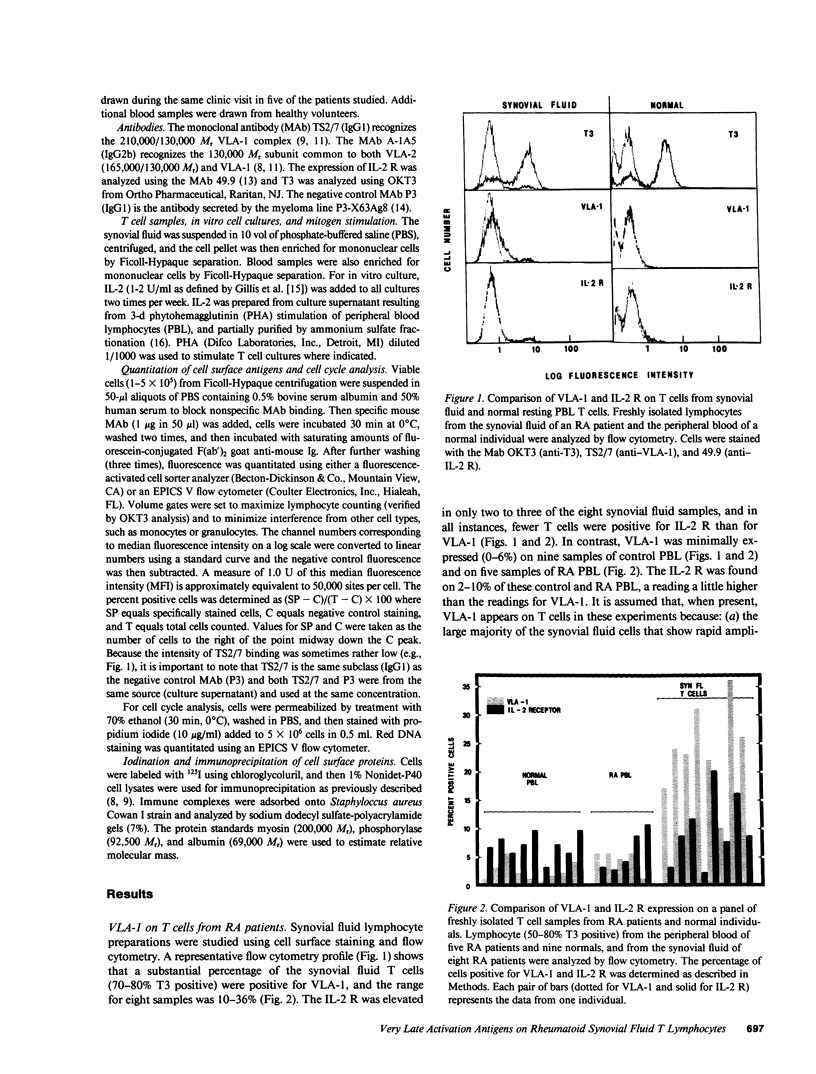
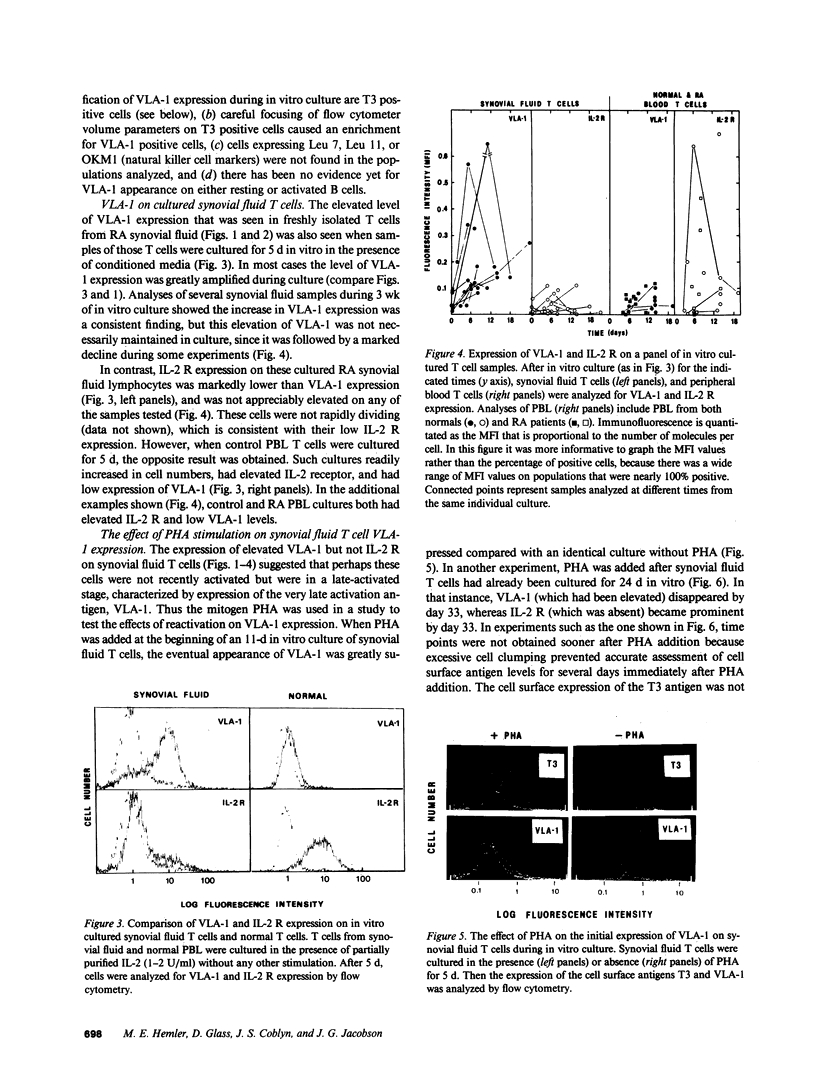
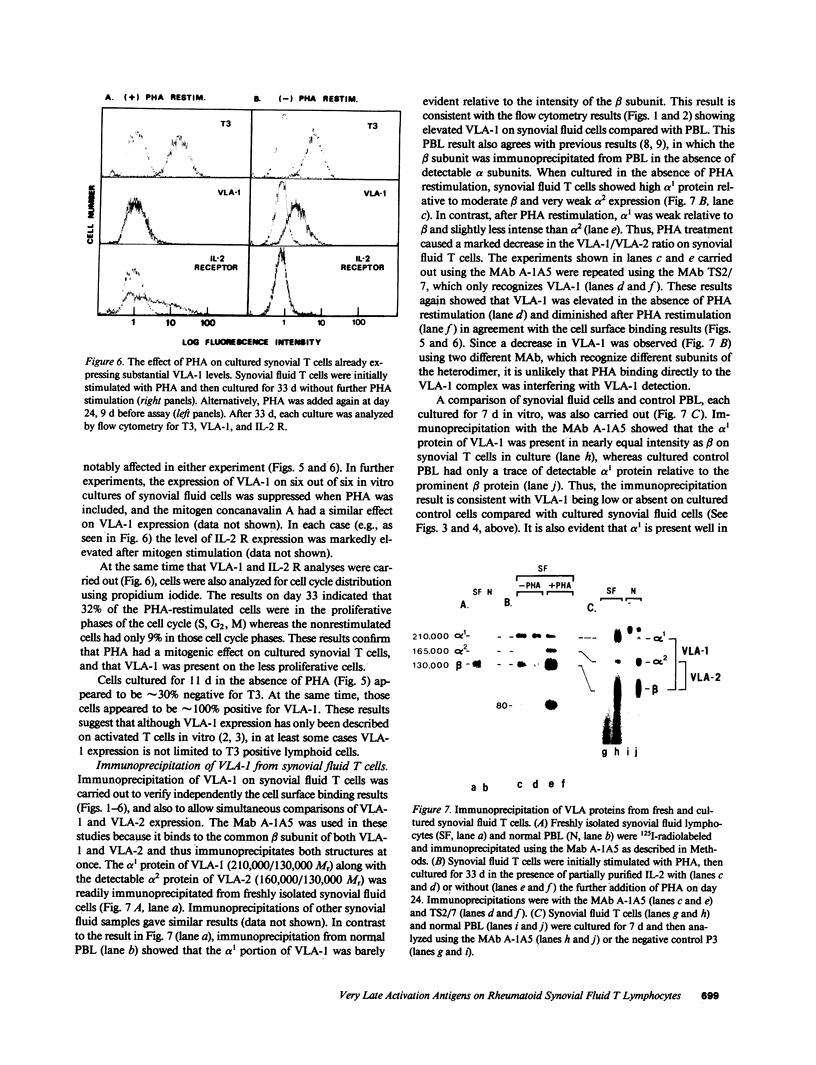
Lymphocytes from the synovial fluid of eight out of eight rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients had elevated very late activation antigen-1 (VLA-1) expression (10-36% positive cells), whereas peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) from RA patients and healthy controls had low VLA-1 expression (0-6% positive cells). During 1-2 wk of in vitro culture, VLA-1 increased on synovial fluid cells but remained low on PBL. In comparison, the interleukin 2 receptor (IL-2 R) was less prominent than VLA-1 on fresh synovial fluid cells, did not increase on cultured synovial fluid T cells, but did increase greatly on cultured PBL. The mitogen PHA reversed or prevented the appearance of VLA-1+, IL-2 R- synovial fluid cells during in vitro culture, thus giving IL-2 R+, VLA-1- cells. These results emphasize that VLA-1+ SF cells are different from resting cells or IL-2 R+ activated PBL T cells, and VLA-1 on synovial fluid T cells may be incompatible with mitogen stimulation. In addition, the VLA-2 heterodimer (165,000/130,000 relative molecular mass [Mr]) was regulated opposite to the VLA-1 heterodimer (130,000/210,000 Mr) on synovial lymphocytes, and thus the VLA-1/VLA-2 ratio is another indicator of the stage of T cell activation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burmester G. R., Jahn B., Gramatzki M., Zacher J., Kalden J. R. Activated T cells in vivo and in vitro: divergence in expression of Tac and Ia antigens in the nonblastoid small T cells of inflammation and normal T cells activated in vitro. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1230–1234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmester G. R., Yu D. T., Irani A. M., Kunkel H. G., Winchester R. J. Ia+ T cells in synovial fluid and tissues of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Nov;24(11):1370–1376. doi: 10.1002/art.1780241106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotner T., Williams J. M., Christenson L., Shapiro H. M., Strom T. B., Strominger J. Simultaneous flow cytometric analysis of human T cell activation antigen expression and DNA content. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):461–472. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson B. L., Faust J., Pessano S., Daniele R. P., Rovera G. Differentiation and activation phenotypes of lung T lymphocytes differ from those of circulating T lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):60–65. doi: 10.1172/JCI111977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R. I., Fong S., Sabharwal N., Carstens S. A., Kung P. C., Vaughan J. H. Synovial fluid lymphocytes differ from peripheral blood lymphocytes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):351–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R. I., Hueniken M., Fong S., Behar S., Royston I., Singhal S. K., Thompson L. A novel cell surface antigen (T305) found in increased frequency on acute leukemia cells and in autoimmune disease states. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):762–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E. A., Robb R. J., Roth J. A., Neckers L. M., Lachman L. B., Wilson D. J., Rosenberg S. A. Lymphokine-activated killer cell phenomenon. III. Evidence that IL-2 is sufficient for direct activation of peripheral blood lymphocytes into lymphokine-activated killer cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1356–1361. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafler D. A., Hemler M. E., Christenson L., Williams J. M., Shapiro H. M., Strom T. B., Strominger J. L., Weiner H. L. Investigation of in vivo activated T cells in multiple sclerosis and inflammatory central nervous system diseases. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1985 Nov;37(2):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(85)90147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E., Jacobson J. G., Brenner M. B., Mann D., Strominger J. L. VLA-1: a T cell surface antigen which defines a novel late stage of human T cell activation. Eur J Immunol. 1985 May;15(5):502–508. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E., Jacobson J. G., Strominger J. L. Biochemical characterization of VLA-1 and VLA-2. Cell surface heterodimers on activated T cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15246–15252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E., Malissen B., Rebai N., Liabeuf A., Mawas C., Kourilsky F. M., Strominger J. L. A 55,000 Mr surface antigen on activated human T lymphocytes defined by a monoclonal antibody. Hum Immunol. 1983 Oct;8(2):153–165. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(83)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E., Sanchez-Madrid F., Flotte T. J., Krensky A. M., Burakoff S. J., Bhan A. K., Springer T. A., Strominger J. L. Glycoproteins of 210,000 and 130,000 m.w. on activated T cells: cell distribution and antigenic relation to components on resting cells and T cell lines. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3011–3018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E., Ware C. F., Strominger J. L. Characterization of a novel differentiation antigen complex recognize by a monoclonal antibody (A-1A5): unique activation-specific molecular forms on stimulated T cells. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):334–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi L., Lehner T., Burry H. C. The response of synovial fluid lymphocytes to T and B stimulants in vitro. Immunology. 1973 Nov;25(5):905–908. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney J. F., Radbruch A., Liesegang B., Rajewsky K. A new mouse myeloma cell line that has lost immunoglobulin expression but permits the construction of antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1548–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klareskog L., Forsum U., Malmnäs Tjernlund U. K., Kabelitz D., Wigren A. Appearance of anti-HLA-DR-reactive cells in normal and rheumatoid synovial tissue. Scand J Immunol. 1981 Aug;14(2):183–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1981.tb00198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluin-Nelemans H. C., van der Linden J. A., Gmelig Meyling F. H., Schuurman H. J. HLA-DR positive T lymphocytes in blood and synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1984 Jun;11(3):272–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mier J. W., Gallo R. C. Purification and some characteristics of human T-cell growth factor from phytohemagglutinin-stimulated lymphocyte-conditioned media. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6134–6138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROPES M. W., BENNETT G. A., COBB S., JACOX R., JESSAR R. A. 1958 Revision of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Rheum Dis. 1958 Dec;9(4):175–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. M., Redelman D., Zvaifler N. J. Studies of rheumatoid synovial fluid lymphocytes. II. A comparison of their behavior with blood mononuclear cells in the autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction and response to TCGF. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Apr;27(1):15–27. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu D. T., Winchester R. J., Fu S. M., Gibofsky A., Ko H. S., Kunkel H. G. Peripheral blood Ia-positive T cells. Increases in certain diseases and after immunization. J Exp Med. 1980 Jan 1;151(1):91–100. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]