Abstract
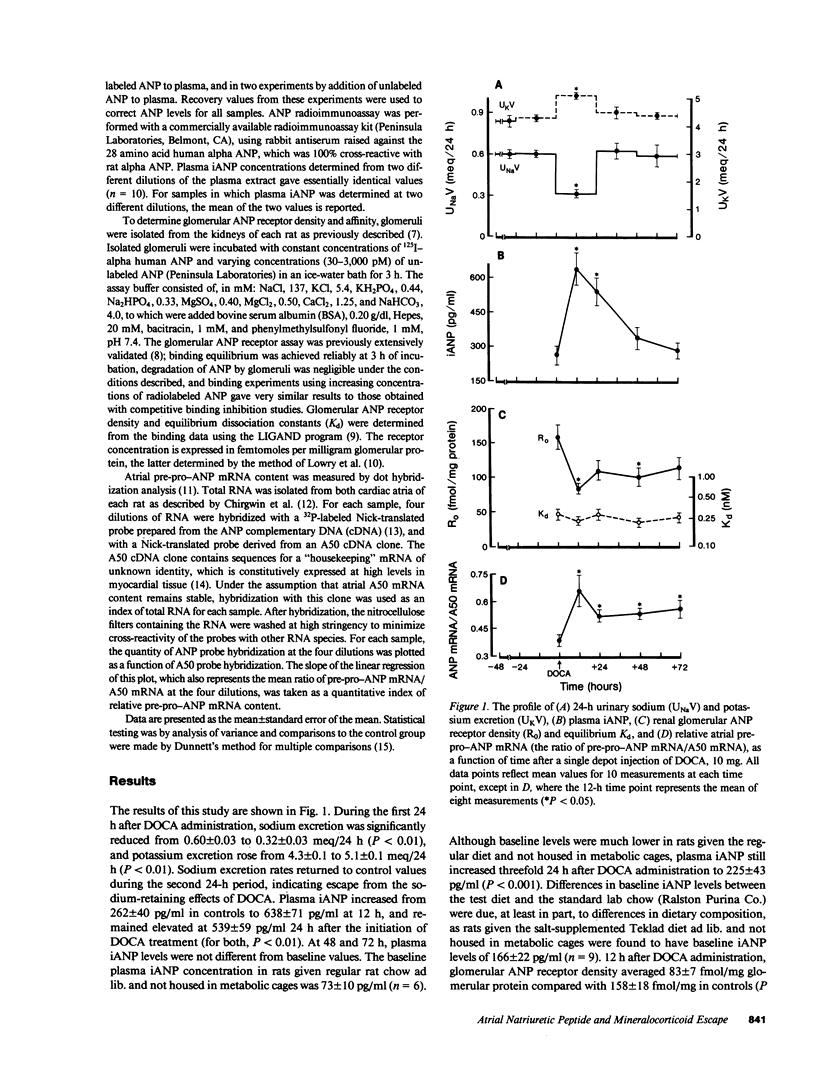
The mechanisms that mediate renal "escape" from the sodium-retaining effects of mineralocorticoids are incompletely understood. This study was undertaken to determine whether atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) may play a role in the escape phenomenon. Immunoreactive ANP in rat plasma increased 2.5-fold above baseline values at 12 and 24 h after a single depot injection of desoxycorticosterone acetate in oil and returned to baseline thereafter. In addition, specific pre-pro-ANP messenger RNA content in rat atria was significantly elevated as early as 12 h after mineralocorticoid administration and remained elevated at 24, 48, and 72 h, indicating a prompt and sustained increase in ANP biosynthesis. Renal glomerular ANP receptor density was down-regulated appropriately with rising plasma ANP levels, and receptor affinity was unchanged. Thus, mineralocorticoid administration in the rat is a powerful stimulus for ANP release and for atrial myocyte ANP synthesis, which suggests a potential role for this hormone in overriding mineralocorticoid-induced renal sodium retention.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballerman B. J., Brenner B. M. Biologically active atrial peptides. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2041–2048. doi: 10.1172/JCI112206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballermann B. J., Hoover R. L., Karnovsky M. J., Brenner B. M. Physiologic regulation of atrial natriuretic peptide receptors in rat renal glomeruli. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2049–2056. doi: 10.1172/JCI112207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett J. C., Jr, Haas J. A., Larson M. S. Renal interstitial pressure in mineralocorticoid escape. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 2):F396–F399. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.249.3.F396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia R., Debinski W., Gutkowska J., Kuchel O., Thibault G., Genest J., Cantin M. Gluco- and mineralocorticoids may regulate the natriuretic effect and the synthesis and release of atrial natriuretic factor by the rat atria in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Sep 16;131(2):806–814. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91311-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gick G. G., Bancroft C. Regulation by calcium of prolactin and growth hormone mRNA sequences in primary cultures of rat pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7614–7618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horký K., Gutkowska J., Garcia R., Thibault G., Genest J., Cantin M. Effect of different anesthetics on immunoreactive atrial natriuretic factor concentrations in rat plasma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jun 28;129(3):651–657. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91941-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox F. G., Burnett J. C., Jr, Kohan D. E., Spielman W. S., Strand J. C. Escape from the sodium-retaining effects of mineralocorticoids. Kidney Int. 1980 Mar;17(3):263–276. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang R. E., Thölken H., Ganten D., Luft F. C., Ruskoaho H., Unger T. Atrial natriuretic factor--a circulating hormone stimulated by volume loading. Nature. 1985 Mar 21;314(6008):264–266. doi: 10.1038/314264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhring J., Möhring B. Reevaluation of DOCA escape phenomenon. Am J Physiol. 1972 Nov;223(5):1237–1245. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.5.1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen H. T., Medford R. M., Nadal-Ginard B. Reversibility of muscle differentiation in the absence of commitment: analysis of a myogenic cell line temperature-sensitive for commitment. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):281–293. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90159-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman C. E., Bloch K. D., Klein K. A., Smith J. A., Seidman J. G. Nucleotide sequences of the human and mouse atrial natriuretic factor genes. Science. 1984 Dec 7;226(4679):1206–1209. doi: 10.1126/science.6542248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman C. E., Duby A. D., Choi E., Graham R. M., Haber E., Homcy C., Smith J. A., Seidman J. G. The structure of rat preproatrial natriuretic factor as defined by a complementary DNA clone. Science. 1984 Jul 20;225(4659):324–326. doi: 10.1126/science.6234658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka I., Misono K. S., Inagami T. Atrial natriuretic factor in rat hypothalamus, atria and plasma: determination by specific radioimmunoassay. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 30;124(2):663–668. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91606-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


