Figure 1. Detection of HIV-1 and Clinical Course Following Analytical Treatment Interruption.
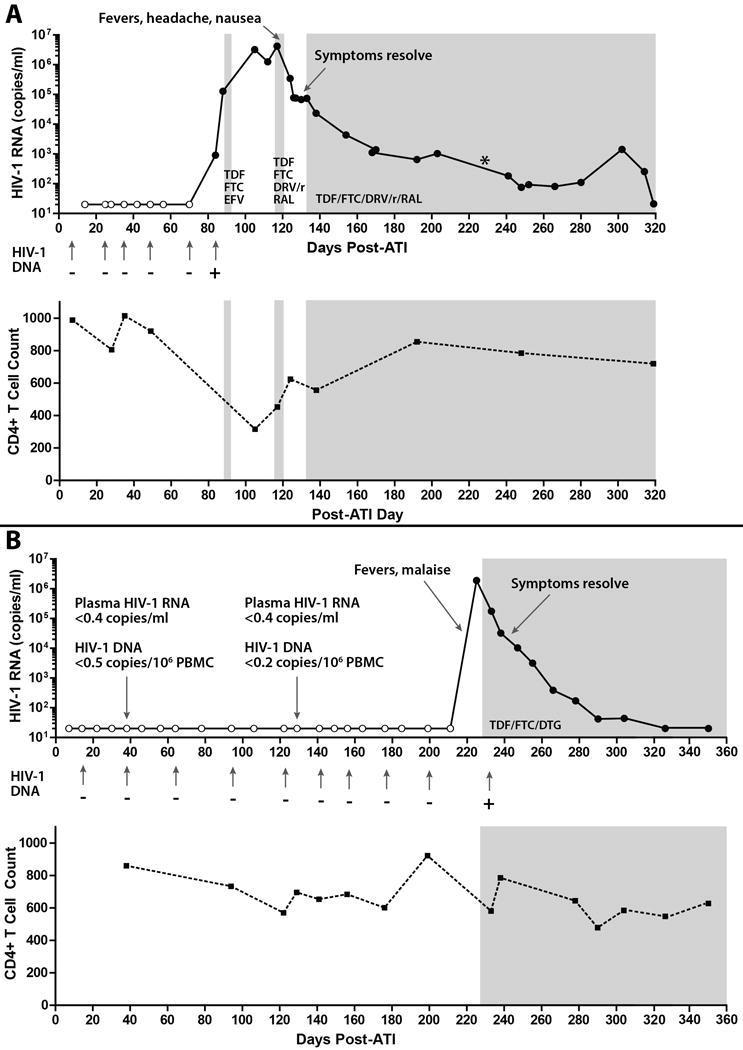
Panel A shows results from clinical monitoring of quantitative HIV-1 plasma RNA and qualitative whole blood HIV-1 DNA testing for patient A. Open circles or minus signs (-) denote samples in which no HIV-1 was detected. Shaded areas represent the use of combination antiretroviral therapy (ART). HIV-1 was first detected 12 weeks after ART interruption (+). Clinical symptoms of acute retroviral syndrome followed a rapid rise in plasma viral load, and resolved at the time of active ART re-initiation. A plasma RNA level of 20, 202 copies/ml was recorded 226 days after treatment interruption (*), but this may have been due to sample switching in the clinical laboratory. CD4+ T cell counts transiently declined during the time of peak viremia.
Panel B shows results for patient B. HIV-1 was first detected 32 weeks after ART interruption. In addition, no HIV-1 DNA or plasma RNA was detected by sensitive research assays 38 and 129 days after ART discontinuation. Clinical symptoms of acute retroviral syndrome occurred approximately 7 days after the last negative viral load test. Symptoms resolved with prompt initiation of ART and subsequent viral suppression. TDF denotes tenofovir; FTC emtricitabine, EFV efavirenz, RAL raltegravir, DRV/r ritonavir boosted darunavir, DTG dolutegravir, ATI analytical treatment interruption.
