Figure 1.
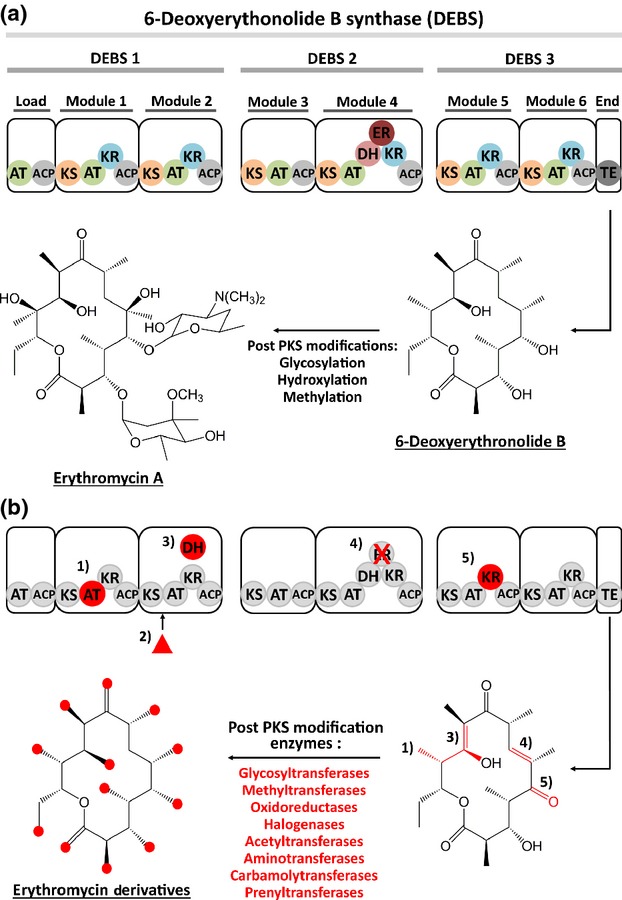
Pictorial illustration of 6-DEBS synthase, a modular type I PKS and successful attempts at engineering this megasynthase. (a) The native biosynthetic gene cluster and end product. (b) Summary of engineered cluster variants and their products; alterations are indicated in red. Manipulation of the polyketide scaffold includes: (1) substitution of domains (Oliynyk et al., 1996); (2) feeding with noncanonical substrates (Jacobsen et al., 1997); (3) domain insertion (McDaniel et al., 1997); (4) inactivation of domains (Donadio et al., 1993); and (5) domain deletions (Donadio et al., 1991). The effects of modifications 1–5 to the 6-dEB scaffold are also indicated in red, as are the positions at which engineered post-PKS tailoring modifications can occur. AT, acetyltransferase domain; ACP, acyl carrier protein domain; KS, ketosynthase domain; ER, enoyl reductase domain; DH, dehydratase domain.
