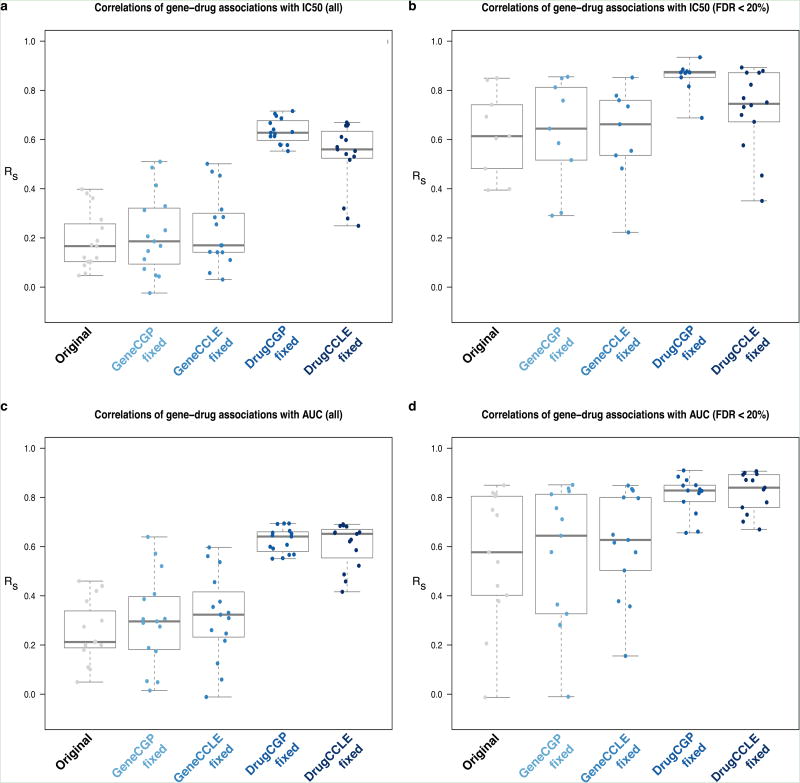
Figure 4.
Effects on consistency by intermixing CCLE and CGP data. The box plots report the correlations between: (a) all and (b) significant (FDR < 20%) gene-drug associations with IC50; (c) all and (d) significant (FDR < 20%) gene-drug associations with AUC. Each box represent the datasets used to compute correlations:‘Original’ refers to the original datasets; ‘GeneCGP.fixed’ refers to [CGPg+CGPd] vs. [CGPg+CCLEd]; ‘GeneCCLE.fixed’ refers to [CCLEg+CGPd] vs. [CCLEg+CCLEd]; ‘DrugCGP.fixed’ refers to [CGPg+CGPd] vs. [CCLEg+ CGPd]; ‘DrugCCLE.fixed’ refers to [CGPg+CCLEd] vs. [CCLEg+CCLEd] where gand d stand for gene expression and drug sensitivity data, respectively.