Abstract
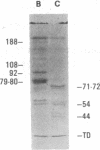
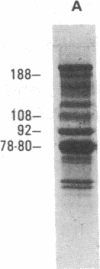
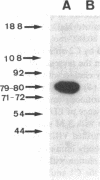
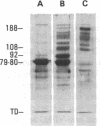
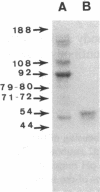
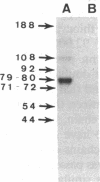
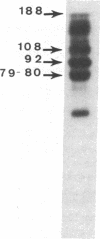
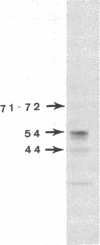
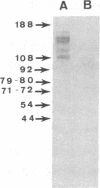
The human Factor VIII procoagulant protein (VIII:C) purified from commercial Factor VIII concentrate consisted of a polypeptide doublet of 80,000 mol wt, a 92,000-mol wt polypeptide, and additional polypeptides of up to 188,000 mol wt. Thrombin digests contained a doublet of 72,000 mol wt, as well as 54,000- and 44,000-mol wt fragments. Proteolysis studies of purified VIII:C using thrombin and activated protein C have suggested that the 92,000- and 80,000 (or 72,000)-mol wt polypeptides comprise activated VIII:C. We have now used seven monoclonal antibodies raised against purified VIII:C to construct a preliminary epitope map of these VIII:C polypeptides. The specific VIII:C polypeptides with which the monoclonal antibodies reacted were determined by immunoblotting of VIII:C onto nitrocellulose sheets after reduced NaDodSO4-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. A minimum of five distinct epitopes were defined by these monoclonal anti-VIII:C antibodies. Identification of polypeptides bearing these epitopes allowed localization of distinct thrombin cleavage sites to the 92,000- and 80,000-mol wt chains, helped define polypeptide chain precursor-product relationships, and suggested that both the 92,000- and 80,000-mol wt polypeptides are necessary for VIII:C function. These data and their interpretation are consistent with the published description of the complete primary structure of VIII:C and its thrombin cleavage products. The 92,000- and 80,000-mol wt chains have been located at the amino- and carboxy-terminal ends of the molecule, respectively.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown J. E., Thuy L. P., Carton C. L., Hougie C. Studies on a monoclonal antibody to human factor viii coagulant activity, with a description of a facile two-site factor VIII coagulant antigen assay. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 May;101(5):793–805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. P., Wright P. W., Hart C. E., Woodbury R. G., Hellström K. E., Hellström I. Protein antigens of normal and malignant human cells identified by immunoprecipitation with monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):4980–4983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church W. R., Jernigan R. L., Toole J., Hewick R. M., Knopf J., Knutson G. J., Nesheim M. E., Mann K. G., Fass D. N. Coagulation factors V and VIII and ceruloplasmin constitute a family of structurally related proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6934–6937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass D. N., Knutson G. J., Katzmann J. A. Monoclonal antibodies to porcine factor VIII coagulant and their use in the isolation of active coagulant protein. Blood. 1982 Mar;59(3):594–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Gardiner J. E., Griffin J. H., Zimmerman T. S. Proteolytic inactivation of human factor VIII procoagulant protein by activated human protein C and its analogy with factor V. Blood. 1984 Feb;63(2):486–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Roberts J. R., Zimmerman T. S. Thrombin proteolysis of purified factor viii procoagulant protein: correlation of activation with generation of a specific polypeptide. Blood. 1983 Apr;61(4):807–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Zimmerman T. S. Characterization of the human factor VIII procoagulant protein with a heterologous precipitating antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant G. A., Keefer L. M., Bradshaw R. A. D-3-Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase from chicken liver. I. Purification. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2724–2726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letter: A more uniform measurement of factor VIII inhibitors. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1975 Dec 15;34(3):869–872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Bohn J. W., Ferry E. L., Yamamoto H., Molinaro C. A., Sherman L. A., Klinman N. R., Katz D. H. Monoclonal dinitrophenyl-specific murine IgE antibody: preparation, isolation, and characterization. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2728–2737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. Radioiodination of proteins by the use of the chloramine-T method. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):210–213. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller H. P., van Tilburg N. H., Derks J., Klein-Breteler E., Bertina R. M. A monoclonal antibody to VIII:C produced by a mouse hybridoma. Blood. 1981 Nov;58(5):1000–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. Determination of total protein. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:95–119. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotblat F., Goodall A. H., O'Brien D. P., Rawlings E., Middleton S., Tuddenham E. G. Monoclonal antibodies to human procoagulant factor VIII. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 May;101(5):736–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sola B., Avner P., Sultan Y., Jeanneau C., Maisonneuve P. Monoclonal antibodies against human factor VIII molecular neutralize antihemophilic factor and ristocetin cofactor activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):183–187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Dahlbäck B., Stenflo J. Thrombin-catalyzed activation of human coagulation factor V. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6556–6564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole J. J., Knopf J. L., Wozney J. M., Sultzman L. A., Buecker J. L., Pittman D. D., Kaufman R. J., Brown E., Shoemaker C., Orr E. C. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding human antihaemophilic factor. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):342–347. doi: 10.1038/312342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veerman E. C., Stel H. V., Huisman J. G., van Mourik J. A. Application of sepharose-linked monoclonal antibodies for the immunoradiometric measurement of factor VIII-procoagulant antigen. Thromb Res. 1984 Jan 1;33(1):89–93. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vehar G. A., Keyt B., Eaton D., Rodriguez H., O'Brien D. P., Rotblat F., Oppermann H., Keck R., Wood W. I., Harkins R. N. Structure of human factor VIII. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):337–342. doi: 10.1038/312337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]