Figure 1.
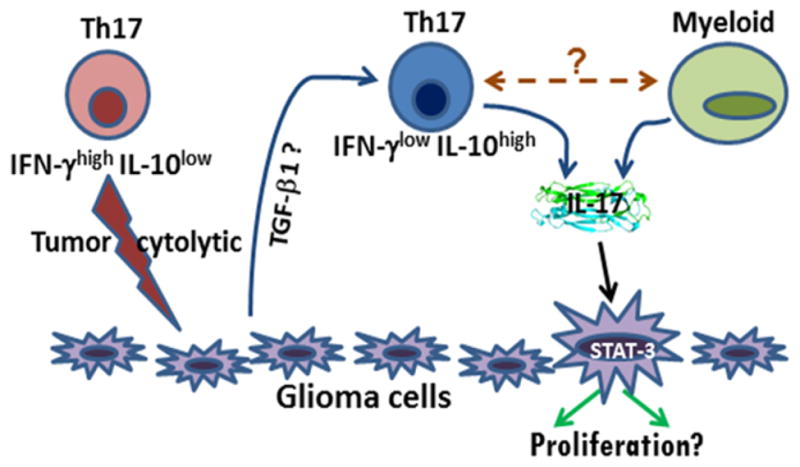
A schematic representation of possible mechanisms of glioma-Th17/IL-17 interaction.
Naïve Th17 cells (or Th17 cells in gliomas with low TGF-β levels) may express high IFN-γ, low IL-10, and show anti-glioma cytolytic activity. On the other hand, glioma derived factors, mainly TGF-β1; inhibit cytolytic activity of glioma-associated Th17 cells. Th17 cells may also influence glioma progression indirectly, via their effect on other immune cells, including MDSCs. Moreover, a small percentage of glioma cells (possibly GSCs) express IL-17R, which, upon interaction with IL-17, could lead to glioma progression via activation of STAT-3 signaling.
