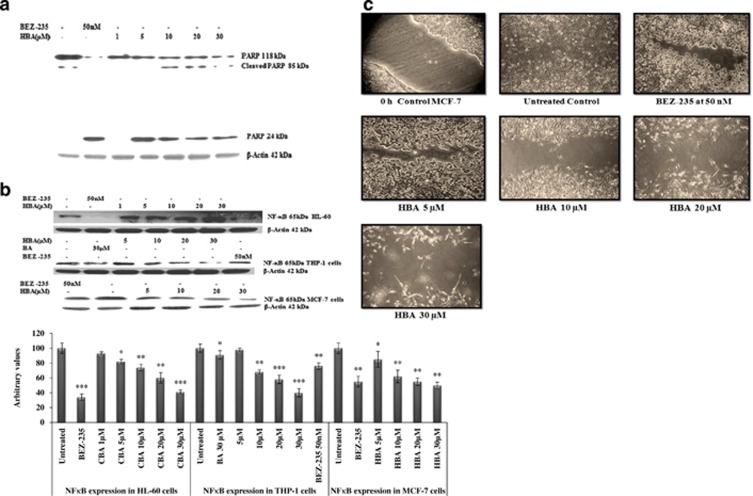
Figure 6.
(a) Influence of HBA on the extent of PARP cleavage and apoptosis. Whole-cell lysate were prepared using HL-60 cells (2 × 106) treated with different concentrations of HBA for the indicated time periods, and 100 μg/ml of protein were subjected to immunoblotting. (b) Influence of HBA on the expression of transcription factor NF-κB. Whole-cell lysate were prepared using HL-60 cells, THP-1 and MCF-7 cells (2 × 106) treated with different concentrations of HBA for the indicated time periods, and 100 μg/ml of protein were subjected to immunoblotting. Specific NFκB antibody was used for the detection of NFκB. Reprobing of the some membrane with the antibody against β-actin did not show any change in the expression of this protein. Data are representative of one of two similar experiments. ***P<0.001, **P<0.01, *P<0.05 versus control using the Student's t-test. (c) In vitro cell migration assay on MCF-7 cells. Briefly cells were seeded in six-well plate. When a tight cell monolayer was formed, a wound was created using a 1000-μl tip, and the cell was then washed three times with PBS to remove cell debris. Cells were then treated with the indicated concentrations of HBA. After the completion of the treatment, fresh medium was added to the cells. The number of cells that migrated toward the wound was visualized using × 10 objective Olympus