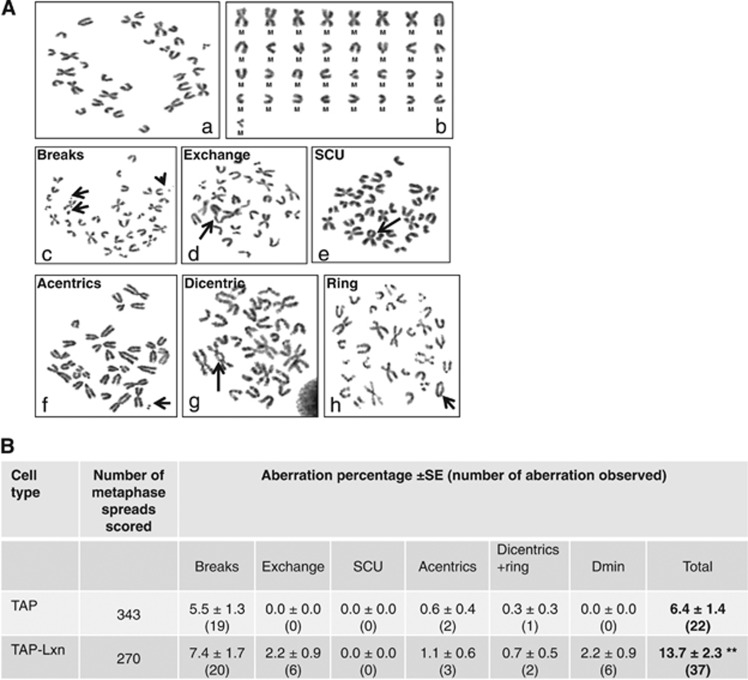
Figure 4.
Lxn increases chromosomal instability. (A) Representative photomicrograph showing different structural chromosomal aberrations. Arrows indicate (a) normal metaphase spread with 33 chromosomes, (b) karyotype of the normal metaphase showing seven metacentric chromosomes, (c) chromatid-type breaks, (d) chromatid-type exchange, (e) sister chromatid union, (f) acentric fragment, (g) dicentric chromosome and (h) ring chromosome. (B) Lxn increases chromosomal aberrations. Aberration percentage±S.E. (total number of aberration observed) detected in TAP control and TAP-Lxn FDC-P1 cells. Standard errors on the aberration percentage were calculated by √a/A, where a is the number under consideration and A is the total number of cells analyzed. The abbreviations used for chromosomal aberrations are according to international nomenclature.47 Z-test was used for group comparison.46 **P<0.01