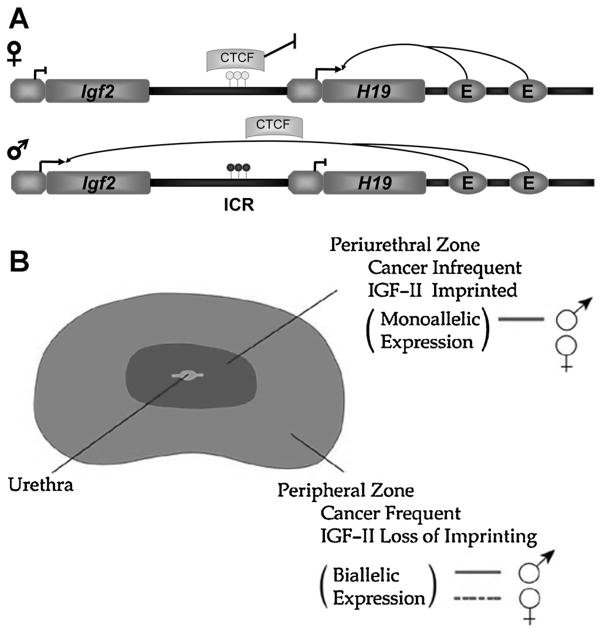
Fig. 1.
Igf2 imprinting. A: Schematic of Igf2-H19 imprint regulation. The imprinted Igf2/H19 locus contains an intergenic imprint control region (ICR) along with shared enhancers that collectively coordinate gene expression. Normal imprinting in this region is characterized by CpG methylation on the paternal allele (lower) within the ICR. This CpG methylation blocks CTCF, a chromatin insulator, binding to Igf2 and facilitates enhancer binding to the Igf2 promoter leading to expression of the gene. CTCF binds hypomethylated CpGs on the maternal allele (upper) at the ICR blocking enhancer binding to the Igf2 promoter and silencing of gene expression. Aging is associated with decreased CTCF levels and altered methylation at the ICR. B: Model of Igf2 imprinting in the human prostate. The perhipheral zone demonstrates the regional loss of imprinting associated with prostate disease that is age-dependent. Cancers commonly form in this region and also demonstrate a loss of imprinting. In the central zone, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is found. Igf2 imprinting is maintained in this region.