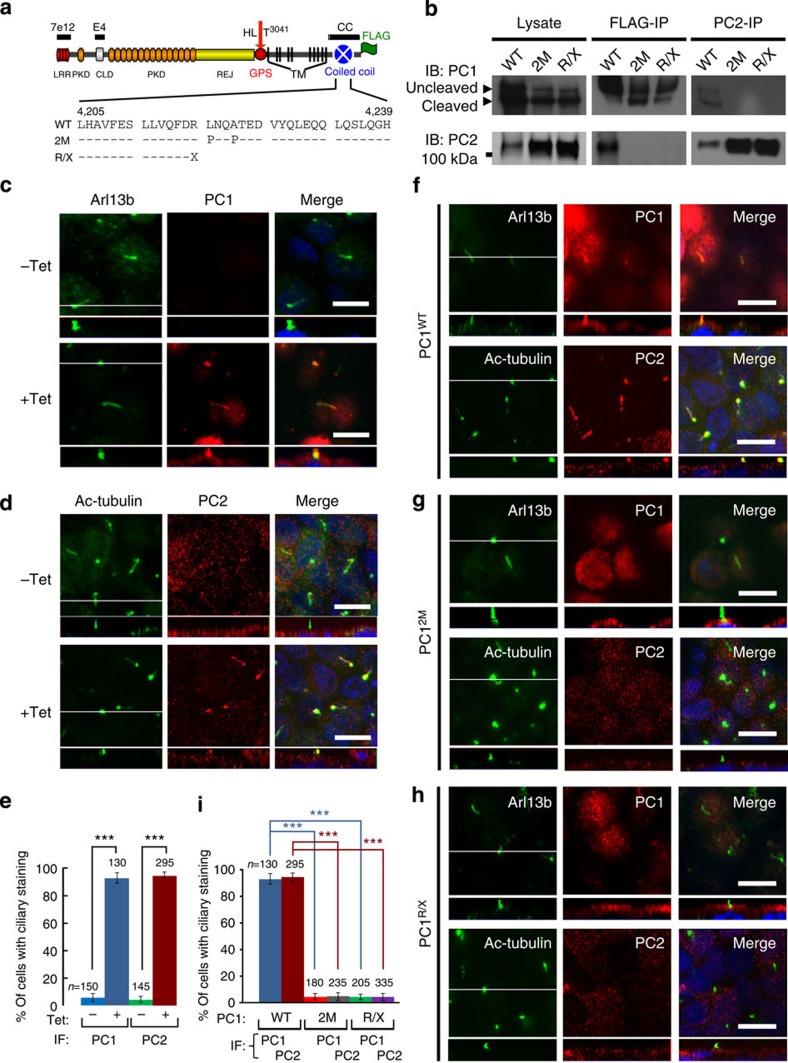
Figure 2. Direct interaction of PC1 and PC2 is required for ciliary localization.
(a) A schematic diagram of the domain organization of mouse polycystin-1 with epitope position of antibodies and FLAG-tag indicated. LRR, leucine-rich repeat; CLD, C-type lectin-binding domain; PKD, polycystic kidney disease repeats; REJ, receptor for egg jelly module; GPS, G-protein-coupled receptor proteolytic site; TM, transmembrane domain. GPS cleavage occurs at HL^T3041. Mutations in the coiled-coil domain are indicated below the wild-type (WT) sequence. (b) Lysates of the induced MDCK cells were subject to reciprocal immunoprecipitation (IP) with the anti-FLAG or anti-PC2. The IP products were analysed by western blotting with antibodies against PC1 (7e12) or PC2 as indicated. (c,d) Confocal images of non-induced (−Tet) or induced (+Tet) MDCKPC1WT cells, stained with antibodies as indicated. The white line in the XY scan indicates the path of the XZ scan. (e) Quantification of PC1 and PC2 ciliary localization for (c,d) from three independent experiments and presented as the mean±s.e.m.; ***P<0.001. The number of cells analysed is indicated. (f–h) Confocal images of induced MDCK cells expressing wild-type or mutant PC1 proteins as indicated, stained with antibodies as indicated. Note that the mutants do not localize to cilia nor induce ciliary localization of endogenous PC2. Scale bar, 10 μm. (i) Quantification of PC1 or PC2 ciliary localization in (f–h) from three independent experiments and presented as the mean±s.e.m.; ***P<0.001. The number of cells analysed is indicated.