Figure 5. Analysis of immune cell infiltration into the spinal cord in naïve and EAE mice after transplantation of bone marrow (BMX) from β-actin-EGFP donor mice.
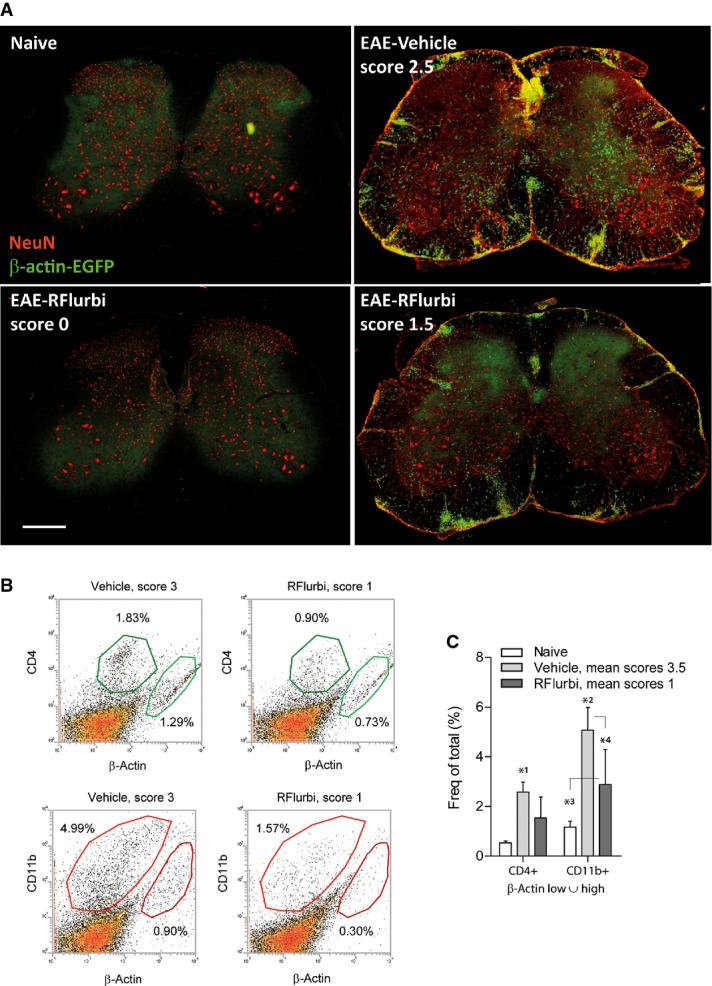
- Immunofluorescence of β-actin-EGFP positive infiltrating cells (green). Neurons were counterstained with the neuronal marker NeuN (red). Scale bars 200 μm. Two extreme examples of the R-flurbiprofen treated group with complete and moderate efficacy are shown.
- Scatter dot plots of the FACS analysis of β-actin-EGFP positive infiltrating T cells (CD4+) and myeloid cells (CD11b+).
- Quantitative results of the ‘β-actin low or high’ gate. Myeloid cell infiltrates were significantly reduced in the R-flurbiprofen group. Further quantitative results are given in Supplementary Table S4. The asterisks indicate statistically significant differences versus naïve and as indicated (two-way ANOVA, post hoc Bonferroni for ‘treatment’, n = 5 per group, P-values *10.0113, *20.000962, *30.0422, *40.0059).
