Figure 2.
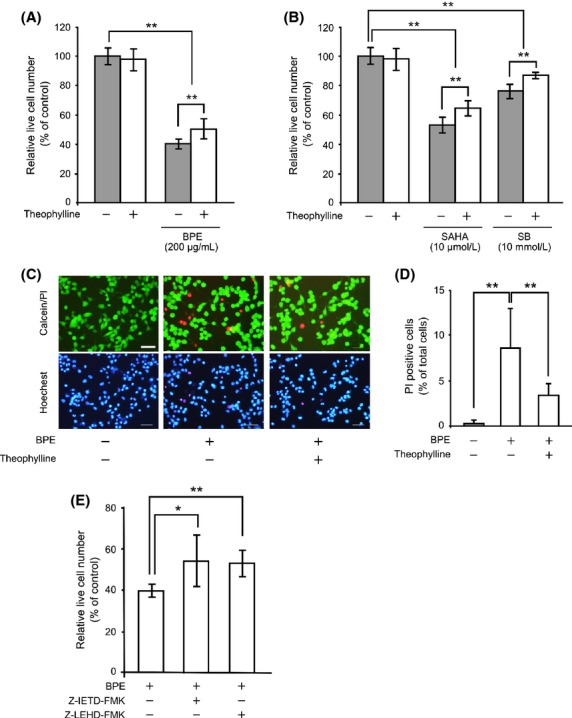
Effects of BPE on cell viabilities and its dependence on Hdac inhibitory activity. Neuro2a cells were treated with 200 μg/mL of BPE (A), 10 μmol/L of SAHA or 10 mmol/L of SB (B) in the presence or absence of 100 μmol/L of theophylline for 24 h. Live cells were counted by the trypan blue exclusion assay. The results are presented as mean ± SD of relative live cell numbers compared to the control (n = 6). **P < 0.01, ANOVA. (C) Typical patterns of the live/dead cell staining subjected Neuro2a cells (Calcein/PI). Nuclei were stained with a Hoechst33342 (Hoechst). Scale bar: 50 μm. (D) Relative ratios of PI-positive dead cells were calculated. The values were represented as the ratio of PI-positive dead cells in total cells ± SD (n = 12). **P < 0.01, ANOVA. (E) Neuro2a cells were treated with 200 μg/mL of BPE in the presence or absence of 10 μmol/L of caspase-8 inhibitor or caspase-9 inhibitor for 24 h. The results are presented as mean ± SD of relative live cell numbers compared to the control (n = 6).*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ANOVA. BPE, Brazilian propolis extract; Hdac, histone deacetylase; SAHA, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid; SB, sodium butyrate; ANOVA, analysis of variance; PI, propidium iodide.
