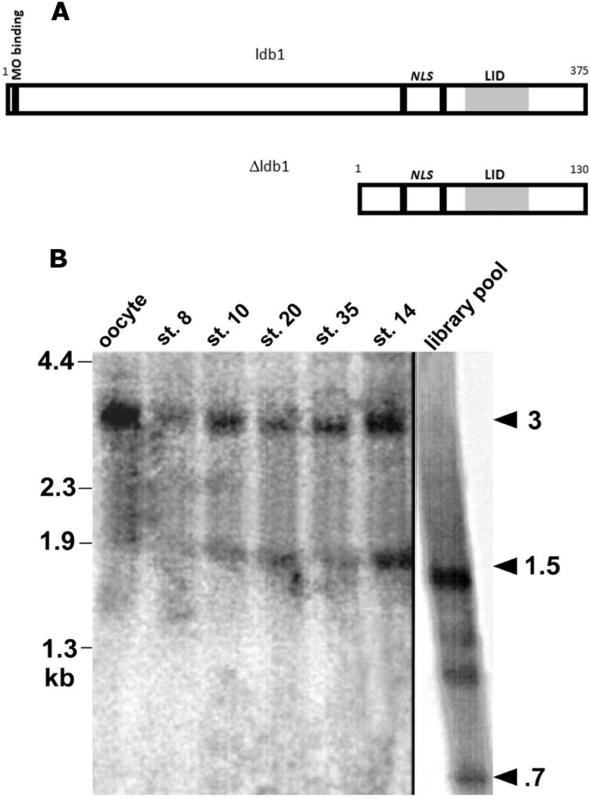
Fig. 1.
A: Comparisons of sizes of Δldb1 fragment and full-length ldb1; nuclear localization signals (NLS) and MO binding site indicated. The functional LIM-binding domain of ldb1/ldb2 (LIM interaction domain, LID) is shaded. B: Northern analysis of endogenous and synthetic transcripts for ldb1 expression (Δldb1 probe). Lanes 1-5: Five embryo equivalents total RNA each from St. VI oocyte, St. 8, St. 10, St. 20, and St. 35 embryos. Lane 6: 1.5 μg St. 14 poly(A)+ RNA. Lane 7: 1 μg pooled synthetic RNA from 10,000 member library fraction. Library pool contains bands corresponding to Δldb1 (700-750 bp) and ldb1 (1.5 kb). Oocyte/embryos contain endogenous 3kb and 1.5-1.8 kb ldb1 transcripts; not Δldb1.