Figure 4.
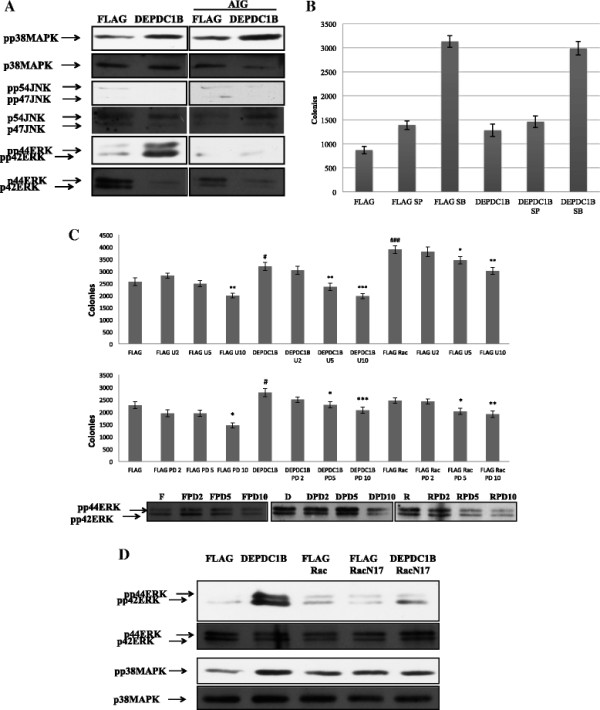
MAPK activity followed KB cells transfected with DEPDC1B expression plasmids. (A) Following the transfection of KB cells with DEPDC1B expression plasmids in adherent and nonadherent culture conditions (AIG), ERK and p38 MAPK activities were induced, whereas JNK activities were suppressed (AIG). 50 μg of total cellular proteins were analyzed using western blotting and probed with specific antibodies. (B) DEPDC1B induced soft agar colony formation not mediated through JNK or p38. KB and KB-DEPDC1B cells were inoculated into soft agar medium containing different concentrations of either SB203580 or SP600125 (10 μM). (C) DEPDC1B induced soft agar colony formation mediated through ERK. KB, KB-DEPDC1B, and KB-DEPDC1B-Rac1 cells were inoculated into soft agar medium containing different concentrations of either U0126 or PD98059 (0, 2, 5, 10 μM). The results are presented as mean ± S.E. *, P < 0.05, **, 0.001 ≤ P < 0.01, ***, P < 0.001. The lower panel indicates the concentration of drug to block activity of ERK and at the concentration of 10 μM PD98059 has the most significant to block ERK activity to 50%. (D) DEPDC1B-enhanced ERK activation was Rac1-dependent. Stable KB cell lines were seeded in a 50-mL conical tube with methylcellulose. Cell lysates were harvested 72 h later. Subsequently, 50 μg of total cellular proteins were analyzed using western blotting and probed with specific antibodies.
