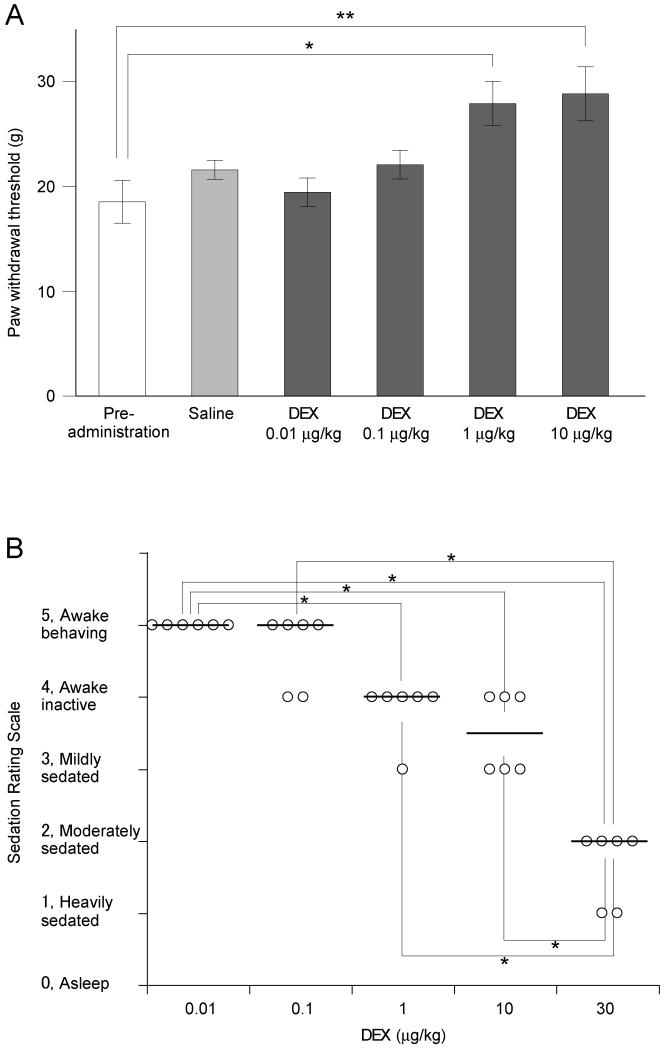
Figure 1. Dose-dependent anti-nociceptive and sedative action of systemic dexmedetomidine.
A) Paw withdrawal thresholds to mechanical stimuli were measured in conscious animals using the Dynamic Plantar Aesthesiometer 20 min after intraperitoneal administration of dexmedetomidine (DEX, 0.01 to 10 μg/kg, n = 13). Dexmedetomidine significantly increased the withdrawal threshold at doses of 1 μg/kg (*p < 0.05) and 10 μg/kg (**p < 0.01) compared control prior to drug administration (n = 13, one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s post hoc test).
B) The sedation rating scores were assessed 20 minutes after intraperitoneal dexmedetomidine (DEX, 0.01 to 10 μg/kg, n = 6). Median scores were significantly decreased at 1 μg/kg (*p < 0.05) and 10 μg/kg (**p < 0.01) compared with pre-administration control (Kruskal-Wallis test followed by the Stell-Dwass test) although most of the animals were considered to be still awake or only mildly sedated in this dose range. Only those animals receiving 30 μg/kg showed evidence of moderate to heavy sedation which was a significantly greater degree of sedation than that produced by either 1 or 10 μg/kg (p < 0.05).