Figure 6.
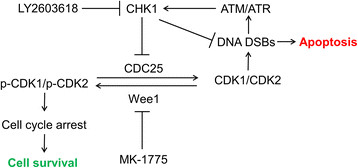
Proposed mechanisms for the anti-leukemic interaction of MK-1775 and LY2603618 in AML cells. MK-1775 inhibits Wee1, leading to decreased inhibitory phosphorylation of CDK1/2, allowing CDK1/CDK2 to remain active. This eventually leads to DNA DSBs which triggers activation of ATM/ATR and activates CHK1. Active CHK1 inhibits CDC25s leading to decreased removal of the inhibitory phosphorylation on CDK1/2, thus limiting the amount of active CDK1/2 and the resulting DNA damage from MK-1775 treatment. The addition of a CHK1 inhibitor (e.g. LY2603618) would inhibit the CHK1 DNA repair pathway, allowing for the DNA damage to accumulate and cause apoptosis.
