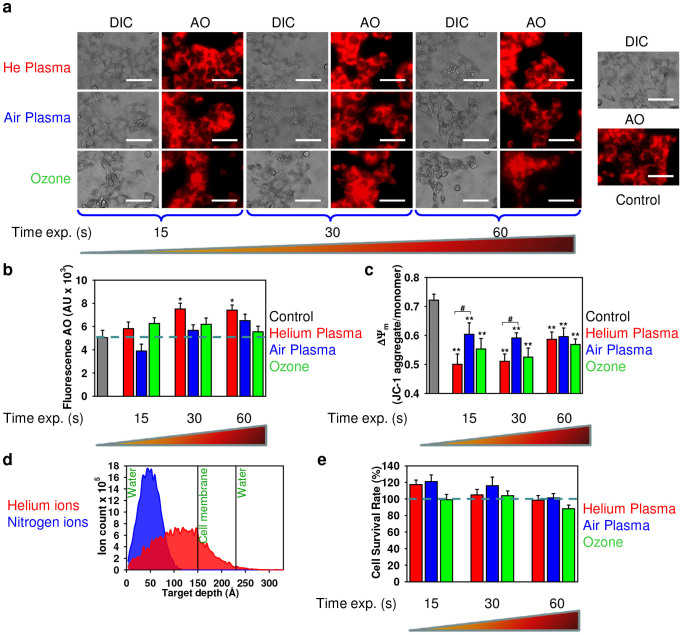
Figure 7. Air, helium plasma and ozone effects on mitochondrial metabolic activity and lysosomal integrity of 3T3 fibroblasts 4 h after treatment.
(a, b) Assessment of plasma effects on lysosomal integrity. After treatment with plasma, cells were stained with AO. AO uptake in acidic lysosomes leads to red fluorescence, which dissipates when the dye leaves this compartment. The accompanying decrease in fluorescence intensity was analyzed with fluorescence microscopy (a) or by spectrofluorometry (b). The results are presented as the mean ± SEM of four independent experiments *P <0.05, **P <0.01 versus controls. Scale bar 100 µm. (c) Mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) state in treated cells with air and helium plasma in comparison with ozone. Cells were stained with JC-1 probe, the JC-1 ratio was measured by spectrofluorometry. The results are presented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments, *P <0.05, **P <0.01 versus controls. (d) Results of SRIM simulations: In-depth profiles of He (red panel) and N (blue panel) ions in the three-layer H2O (10 nm)/membrane (8 nm)/H2O (10 nm). The total number of ions is 10000. (e) ROS scavenger prevents the cytotoxicity induced by air, helium plasma or ozone. Treatment with ROS scavenging agent 5 mM N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) completely abolished the cytotoxicity of air, helium plasma and ozone 24 h after exposure. Cell viability as detected by the WST-1 assay of 3T3 fibroblasts exposed to air, helium plasma or ozone for indicated periods of time. The data were normalized to control values (no plasma or ozone exposure), which were set as 100% cell viability. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 versus controls, mean ± SEM, n = 4.