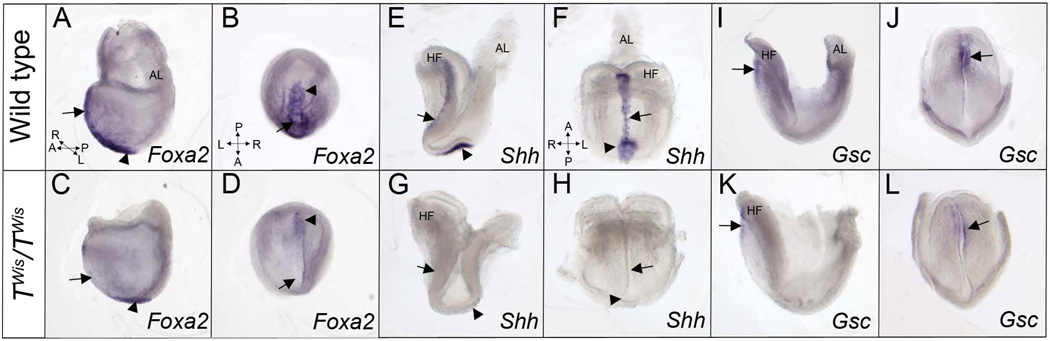
Figure 3. Molecular differentiation of the node and anterior midline in wild type and TWis/TWis embryos at E8.0.
A–D: Left lateral and ventral views of wild type (A, B) and TWis/TWis mutant (C, D) embryos showing expression of Foxa2 by in situ hybridization. Wild type embryos express Foxa2 in the midline and node while TWis/TWis mutant embryos show expression in the node but not in the midline. E–H: Left lateral and frontal views of wild type (E, F) and TWis/TWis mutant embryos (G, H) showing expression of Shh in the node and midline of wild type embryos but no expression in the mutant embryos. I–L: Left lateral and frontal views of wild type embryos (I, J) and TWis/TWis mutant embryos (K, L) showing Gsc expression in the anterior foregut endoderm and prechordal plate in wild type embryos and a similar pattern but lower expression level in mutant embryos. Arrows point to the anterior midline and arrowheads point to the node. Compass in A refers to A, C, E, G, I, K; compass in B refers to B, D, J, L; compass in F refers to F, H. AL, allantois; HF, headfolds.