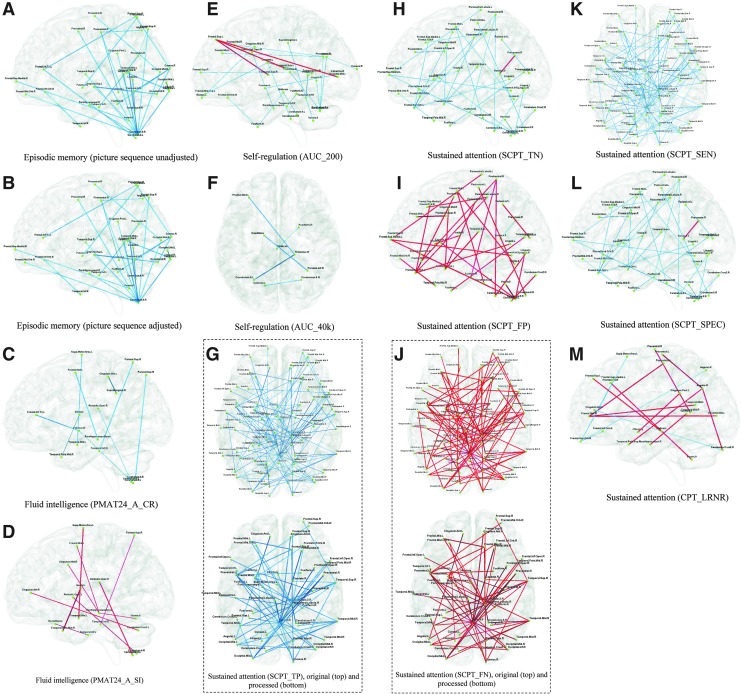
FIG. 10.
Paths whose MTSTs significantly predicted variability in selected behavioral measures. The predictive ability is quantified by the regression coefficient α for each MTST in the GLM shown in Equation 4 in the main text. The coefficient α is passed through a z-test and Bonferroni corrected for multiple comparisons (corrected p<0.05). In each subfigure, cobalt blue paths have negative α values, and red paths have positive α values. The behavior tests for subfigures are as follows: (A) Episodic memory (picture sequence test, unadjusted). (B) Episodic memory (picture sequence test, adjusted). (C) Fluid intelligence (PMAT24_A_CR). (D) Fluid intelligence (PMAT24_A_SI). (E) Self-regulation (AUC_200). (F) Self-regulation (AUC_40k). (G) Sustained attention (SCPT_TP). The top one is the original figure. Since it has too many paths that hamper visualization, we show the processed figure as the bottom one with only paths that connect to nodes with five or more paths. (H) Sustained attention (SCPT_TN). (I) Sustained attention (SCPT_FP). (J) Sustained attention (SCPT_FN). The top one is the original figure. Since it has too many paths that hamper visualization, we show the processed figure as the bottom one with only paths that connect to nodes with five or more paths. (K) Sustained attention (SCPT_SEN). (L) Sustained attention (SCPT_SPEC). (M) Sustained attention (CPT_LRNR). Please refer to Supplementary Table S2 for details about specific metrics referred to for each behavior. GLM, general linear model.