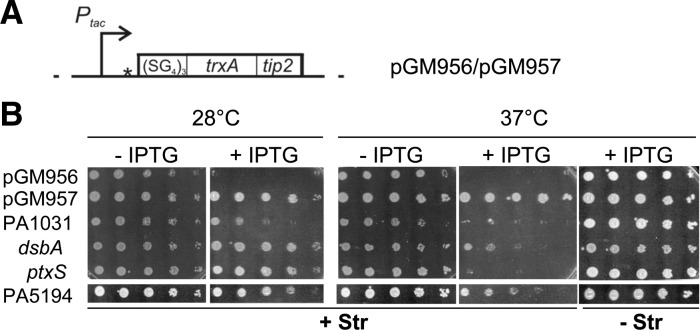
FIGURE 2.
Plating efficiency at different temperatures of clones carrying putative RNATs in TIP2 fusions. (A) Map of the plasmid constructs encoding ST-TIP2. ST-TIP2 is composed by a flexible (SG4)5 linker at the N-terminus, followed by an E. coli TrxA-Tip2 fusion that effectively induces TetR (Goeke et al. 2012). pGM956 and pGM957 differ by the presence in the former of an in-frame TIR driving translation of ST-TIP2, which is absent in pGM957. Details about plasmid construction and coordinates of the cloned regions are reported in Materials and Methods. (Dotted lines) vector sequence; (bent arrows) IPTG-inducible promoter Ptac; (open box) ST-TIP2 ORF; (star) SmaI restriction site exploited for P. aeruginosa DNA cloning in pGM957. (B) Thermosensitive-streptomycin resistance upon induction of TIP2-tagged protein expression. Serial 10-fold dilutions of C-5920 overnight cultures carrying putative P. aeruginosa RNATs cloned upstream of ST-TIP2 in pGM957 were replicated on LD-chloramphenicol plates in the presence or absence of streptomycin (Str) and IPTG and incubated for 16–20 h at the indicated temperatures. C-5920 carrying pGM956 and pGM957 were used as positive and negative controls, respectively, of ST-TIP2 dependent rpsL+ expression.