Figure 1.
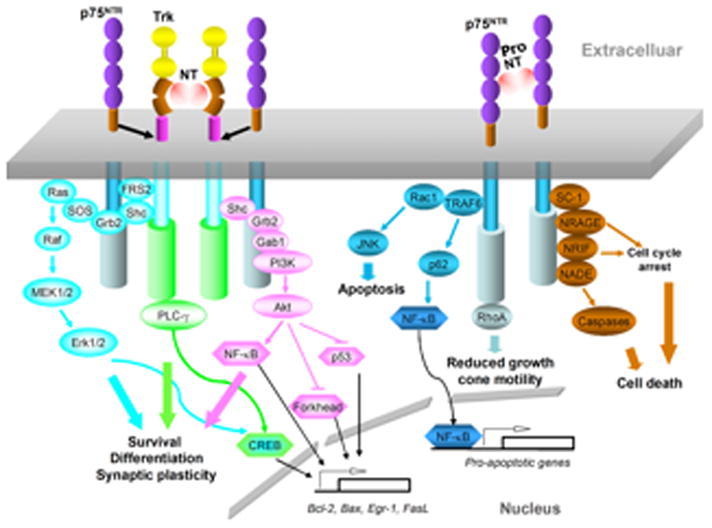
Signaling cascades mediated by Trk receptors and p75NTR. Trk family members recruit and increase the phosphorylation of PLC-γ and Src homologous and collagen-like adaptor protein (Shc), which leads to activation of PI3K and Erk, and participate in cell survival, differentiation, and synaptic plasticity, respectively. Collaboration of p75NTR with Trk augments the Trk effects. In the absence of Trk, p75NTR predominantly signals to activate NF-κB and Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and modulates RhoA activity. Pro-neurotrophins also preferentially bind to the p75NTR signaling apoptotic pathways. These responses are mediated through adaptor proteins that bind to the cytoplasmic domain of p75, including neurotrophin-receptor interacting factor (NRIF), neurotrophin-associated cell death executor (NADE), neurotrophin-receptor-interacting MAGE homolog (NRAGE), and Schwann cell 1 (SC1), which can exert effects on apoptosis, growth cone collapse and cell cycle arrest. Akt, protein kinase B; FRS2, fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 2; Gab1, Grb2-associated binder-1; Grb2, growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/Erk kinase; SOS, Son of Sevenless; TRAF6, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6.
