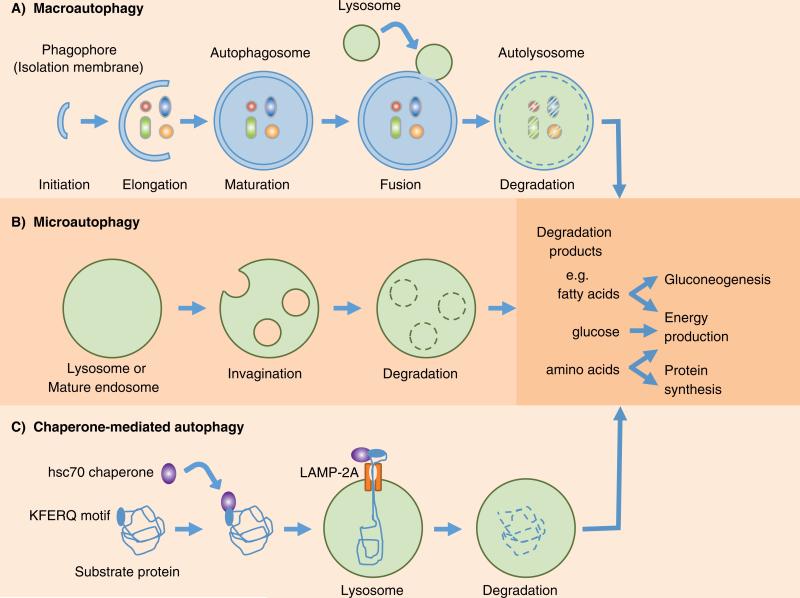
Fig. 1.
Schematic diagram of the three major types of autophagy. (A) Macroautophagy (generally referred as autophagy) initiates with the formation of the phagophore (isolation membrane) around cytosolic components and sequestration by double-membraned vesicles called autophagosomes. Fusion with lysosomes form autolysosomes and the sequestered components are degraded and recycled. (B) In microautophagy, the lysosomes directly engulf cytosolic contents for degradation through invaginations of the lysosomal membrane and internalization of single-membraned vesicles. (C) Chaperone-mediated autophagy selectively degrades proteins containing KFERQ motif that are recognized by the heat shock cognate protein of 70kDa (hsc70) chaperone, and transported into lysosomes via cooperation with lysosome-associated membrane protein-2A (LAMP-2A).