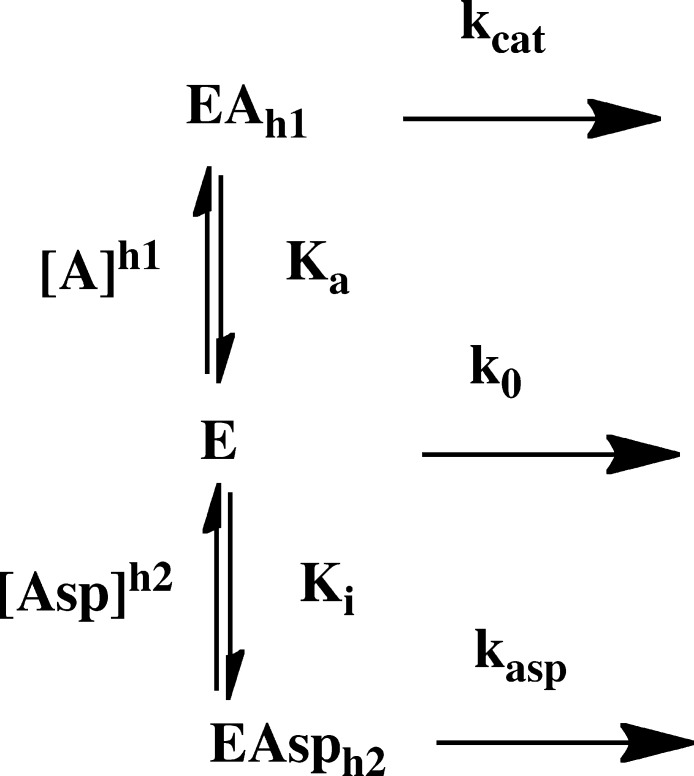
Figure 2.
Reaction scheme showing the proposed inhibitory mechanism of pyruvate carboxylating activity by l-aspartate in the presence of acetyl-CoA, where k0 and kcat are catalytic rate constants for the acetyl-CoA-independent and -dependent reactions catalyzed by the enzyme (E) and enzyme·acetyl-CoA complex (EAh1), respectively. The catalytic rate constant for the reaction catalyzed by the enzyme·l-aspartate complex (EAsph2) is kasp. Ka is the apparent dissociation constant of the EAh1 complex, and h1 is the Hill coefficient for the activation process. Ki is the apparent dissociation constant of the enzyme·l-aspartate complex (EAsph2), and h2 is the Hill coefficient for the inhibition by l-aspartate.