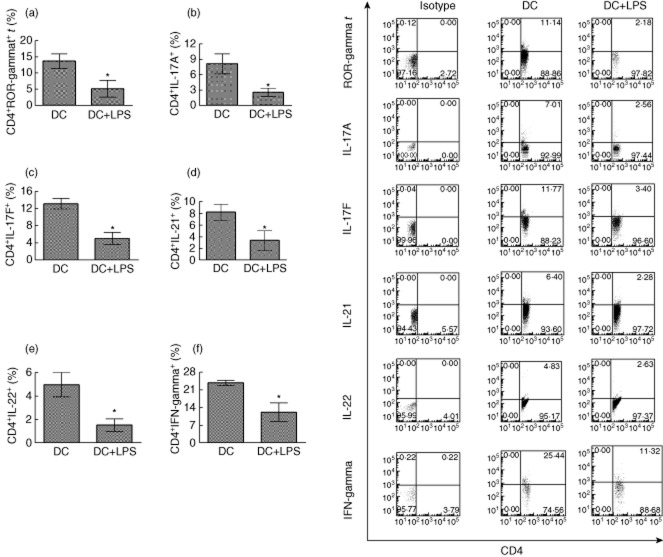
Fig. 3.
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated dendritic cells (DCs) down-regulate expression of retinoic acid-related orphan receptor gamma t (ROR-γt) and multiple cytokines in CD4+ T cells in vitro. Bone marrow DCs pulsed with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) peptide at 0·1 μM were treated with or without LPS stimulation at 1 μg/ml for 24 h. DCs were co-cultured with MOG-primed CD4+ T cells for 3 days. CD4+ T cells were harvested and gated. Expression of ROR-γt (a), interleukin (IL)-17A (b), IL-17F (c), IL-21 (d), IL-22 (e) and interferon (IFN)-γ (f) on CD4+ cells was detected. Error bars represent the mean and standard deviation of triplicate determinations of percentage of CD4+ T cells in three independent experiments (n = 3, t-test, *P < 0·05).